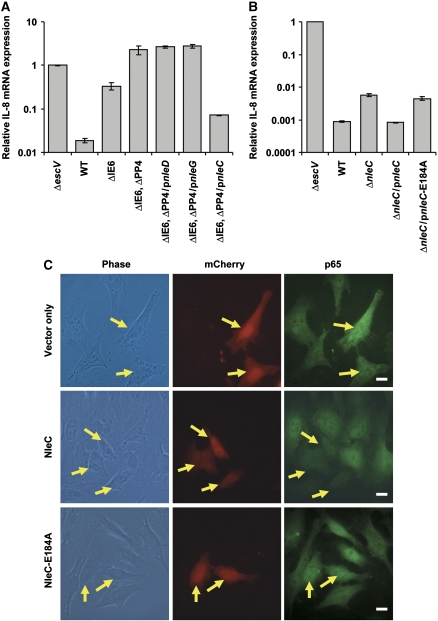
Figure 4.
NleC expression correlates with inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. (A) Deletion analysis to identify the EPEC gene that represses IL-8 induction. HeLa cells were infected with one of the following EPEC: EPEC with a deleted IE6 region (ΔIE6), EPEC with deleted IE6 and PP4 regions (ΔIE6 and ΔPP4), or the latter complemented with plasmids expressing either wild-type NleD, NleG, or NleC (pnleD, pnleG, and pnleC, respectively). Cells infected with TTSS mutant (ΔescV) and wild-type EPEC (WT) served as negative and positive controls, respectively. HeLa cells were infected with the relevant EPEC for 2 h to allow injection of effectors before stimulation with TNFα for 3 h. Then RNA was extracted from the HeLa cells and real-time PCR performed to quantify IL-8 mRNA levels. Experiments were performed in duplicates and a typical experiment out of three is shown. Error bars indicate s.d. (B) NleC is required for inhibition of TNFα-induced IL-8 expression. HeLa cells were infected with nleC mutant, or this mutant complemented with plasmids expressing wild-type NleC (pnleC) or NleC-E184A mutant (pnleC-E184A). TTSS mutant (ΔescV) or wild-type EPEC (WT) served as negative and positive controls, respectively. HeLa cells were infected with these strains as described in (A), RNA was extracted from the HeLa cells and real-time PCR performed to quantify IL-8 mRNA levels. The indicated values are relative to IL-8 RNA levels in cells infected with ΔescV mutant. Experiments were performed in duplicates and a typical experiment out of four is shown. Error bars indicate the s.d. (C) NleC reduces p65 levels in vivo. HeLa cells transfected with plasmid expressing mCherry, mCherry–NleC or mCherry–NleC-E184A (red) were treated with TNFα for 30 min, after which they were fixed and visualized using anti-p65 antibody (green). Yellow arrows indicate cells expressing mCherry proteins. Bar represents 20 μm.