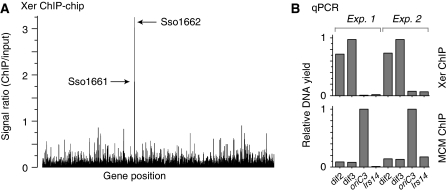
Figure 3.
Identification of the Xer-binding ‘dif' locus in S. solfataricus. Xer was immunoprecipitated from formaldehyde-fixed and sonicated S. solfataricus P2 cell extracts, and bound DNA was analysed by the ‘ChIP-chip' method and by quantitative real-time PCR. (A) ChIP-chip data for anti-Xer ChIP reactions, indicating the peak heights for ORFs SSO1161 and SSO1662, which show a significant enrichment above background. (B) qPCR analysis of anti-Xer and anti-MCM ChIP reactions, using the four indicated primer sets (dif2, dif3, oriC3 and lrs14), in two sets of independent experiments. ‘Input' DNA, purified from the cell extract used in the chromatin immunoprecipitations, was used to generate standard curves in quantification. Data were normalized to the highest yielding sample for each ChIP. The anti-MCM ChIP serves as a control reaction, in which MCM was expected to bind preferentially to origin DNA. The lrs14 control locus was expected not to bind specifically to either MCM or Xer.