Fig. 3.
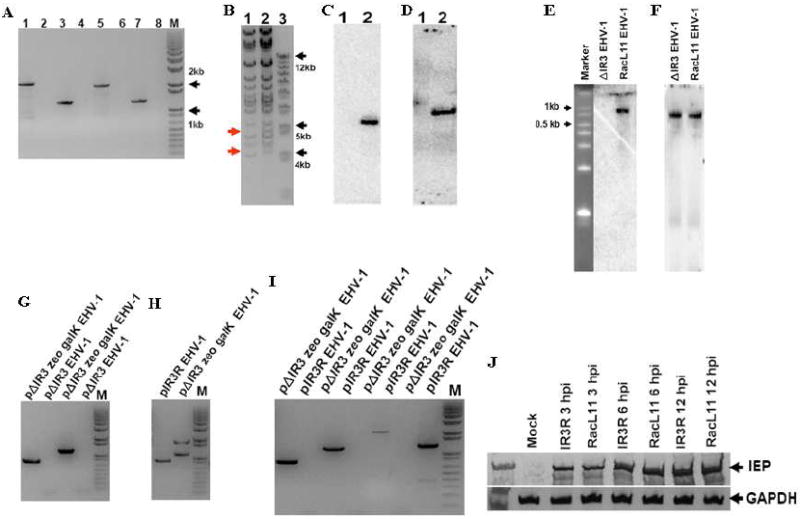
Insertion of zeoR and kanR markers into the EHV-1 genome, and confirmation that ΔIR3 EHV-1 lacks expression of the IR3 transcript. PCR, BamHI digestion, northern blot, and southern blot analyses were performed as described in Materials and Methods. (A) PCR amplification of marker flanking sequences of pΔIR3 EHV-1. pΔIR3 EHV-1 template (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7). pRacL11 EHV-1 template (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8). KanR left flanking region amplification primer set (lanes 1 and 2). KanR right flanking region amplification primer set (lanes 3 and 4). ZeoR left flanking region amplification primer set (lanes 5 and 6). ZeoR right flanking region amplification primer set (lanes 7 and 8). “M” is DNA size marker. (B) BamHI digestion pattern of pΔIR3 EHV-1 BAC DNA. Lanes 1 and 2 represent pRacL11 EHV-1 BAC and pΔIR3 EHV-1 BAC, respectively. (C and D) Southern blot analyses of BamHI digested pΔIR3 EHV-1 BAC DNA by using probes specific for zeoR (C) and kanR (D) genes. Lanes 1 and 2 indicate pRacL11 EHV-1 and pΔIR3 EHV-1 BAC DNA, respectively. (E and F) Northern blot analysis to confirm the absence of the IR3 transcript in ΔIR3 EHV-1 infected cells by using a probe specific for the IR3 transcript (E), and a probe specific to IR5 transcript as a positive control (F). (G, H and I) The PCR amplifications of marker flanking sequences to confirm 1). the insertion of galK marker by using galK marker left and right flanking sequence specific primer sets (G), 2). the removal of galK and zeoR markers by using IE intron flanking sequence specific primer set (H) and 3). the presence of galK and zeoR markers by using primer sets specific to galK and zeoR marker flanking sequences (I). (J) Comparison of the IE protein expression from RK13 cells infected with RacL11 EHV-1 and IR3R EHV-1 (at m.o.i of 10) during immediate-early, early, and late times of EHV-1 replication.
