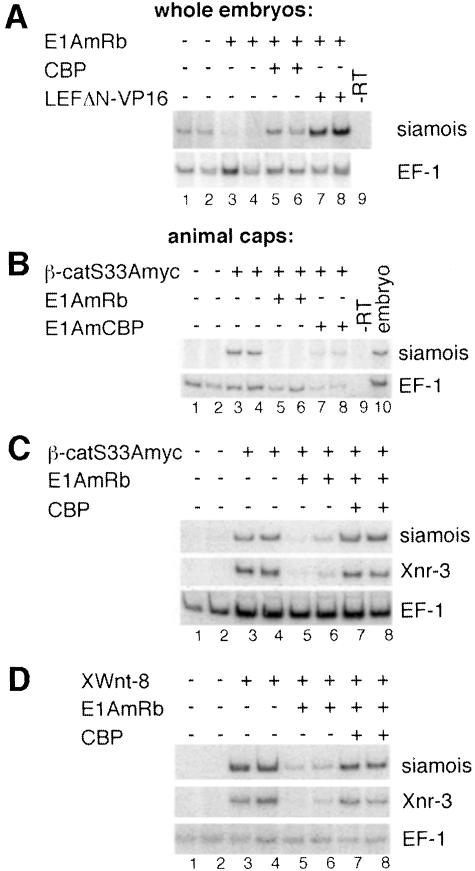
Fig. 7. Transcriptional activation of β-catenin target genes is sensitive to E1A and can be rescued by CBP. (A) RT–PCR analyses of siamois expression in whole embryos after injection of RNAs for E1AmRb (0.5 ng), LEFΔN–VP16 (0.1 ng) and CBP (2.0 ng) into the dorsal vegetal zone of four-cell stage embryos as indicated. Control reactions were performed with an RNA sample not treated with reverse transcriptase (–RT). (B) RT–PCR analyses of ectopic siamois induction in animal cap explants by injection of 0.5 ng of β-catS33Amyc RNA with or without 2.0 ng of E1AmCBP or E1AmRb RNA. Control reactions were performed with RNA from total embryos or RNA samples that were not treated with reverse transcriptase (–RT). (C and D) Expression of CBP restores β-catenin target gene induction in the presence of E1AmRb. RT–PCR analyses of siamois and Xnr-3 expression induced in animal cap explants by injection of 0.5 ng of β-catS33Amyc RNA (C) or 40 pg of XWnt-8 RNA (D) with or without 0.5 ng of E1AmRb RNA and 2.0 ng of CBP RNA. In (D), the various RNAs were applied by two consecutive injections to ensure an overlapping spatial protein distribution of E1A or CBP and the secreted XWnt-8. (A–D) For each RNA combination two embryos or two pools of animal cap explants were analyzed separately. EF-1 expression was monitored as control for RNA amount and integrity.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.