Fig. 4.
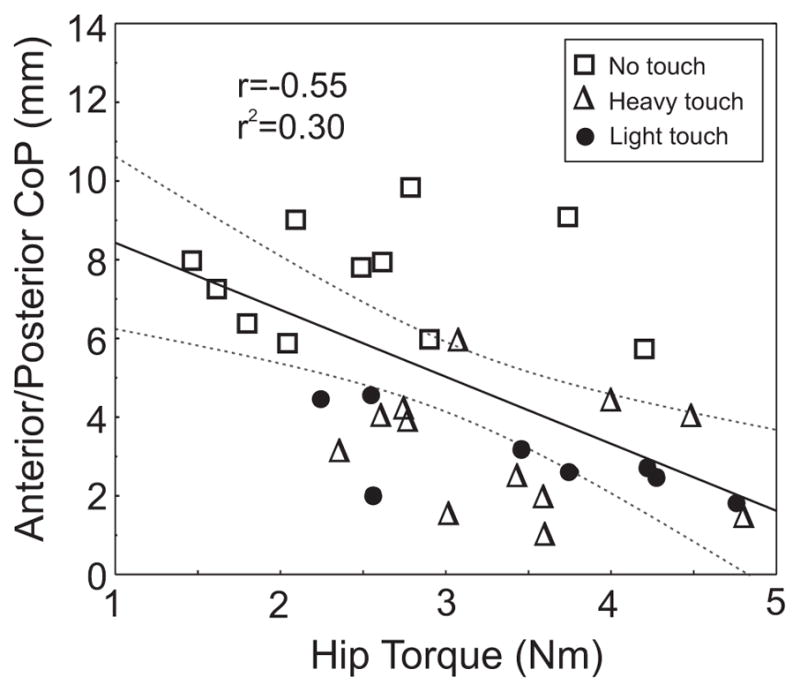
Relation between the hip torque and the center of pressure (CoP) in the anterior/posterior direction during no touch, light touch and heavy touch conditions. The peak-to-peak torque magnitude is inversely related to the root mean square (RMS) of the CoP in the anterior/posterior direction in healthy adults across all three conditions. Regression line (solid line) and 95% confidence interval (dashed line) are displayed.
