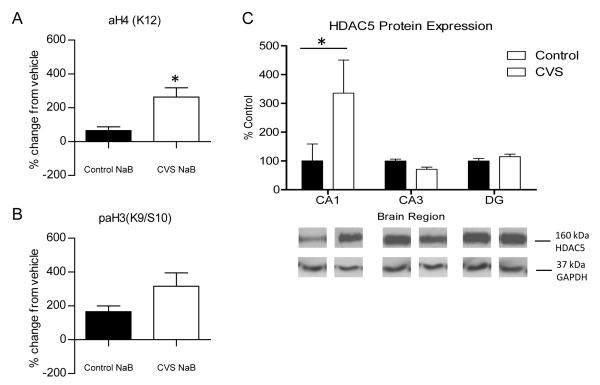
Figure 4.
Deacetylation of histones by Class I/II Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) in control and CVS-treated hippocampus. Western blot analysis of changes in histone 3 and histone 4 acetylation in response to HDAC inhibition in whole hippocampus slices from control and chronic variable stress (CVS) animals treated for one hour with either vehicle or 300 μm sodium butyrate (NaB). (A) Quantification of percentage change from vehicle treated slices in acetylation of lysine 12 on histone 4 [aH4(K12)]. A significant increase from vehicle in K12H4 acetylation was observed in CVS animals compared to control animals. (B) Phospho-acetylation of lysine 9/serine 10 on histone 3 [paH3(K9/S10)] quantification of percentage change mediated by NaB compared to vehicle treated slices. No significant change from vehicle was observed in CVS animals compared to control animals. (C) Quantification and representative western blots from nuclear protein extracted from subdissected hippocampus tissue from control and CVS animals. A significant increase in histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) protein expression was observed in the CA1 region of CVS animals compared to control animals with no change in either CA3 or DG. Representative western blot of GAPDH protein expression are shown as a loading control. Data are shown as means ± SE; *P<0.05 vs. control (n=4 animals per group).