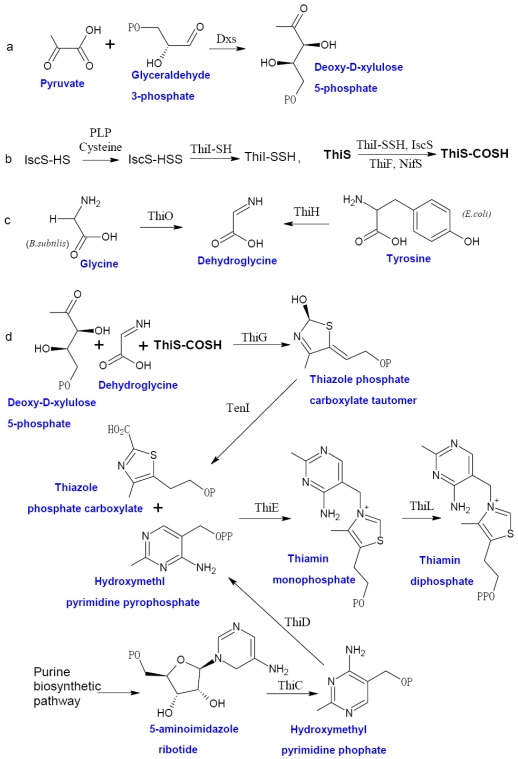
Figure 1.
The biosynthesis of thiamin in bacteria. The thiazole moiety of thiamin is derived from an oxidative condensation of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) (a), cysteine (b), and glycine or tyrosine (c). When the thiazole and pyrimidine moieties are formed, ThiE will coupled them to be thiamin monophosphate and followed by a phosphorylation step to give ThDP (d). Abbreviation: Dxs, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase; ThiF, adenyltransferase; ThiS, sulfur carrier protein; ThiG, thiazole synthase, ThiO, glycine oxidase; ThiH, thiazole synthase; ThiI, sulfur transferase; ThiC, hydroxymethyl pyrimidine synthase; ThiD, hydroxymethyl pyrimidine (phosphate) kinase; NifS, sulfur donor; TenI, transcriptional regulator TenI; IscS, cysteine desulfurase; ThiE, thiamin phosphate synthase; ThiL, thiamin phosphate kinase. This figure is modified from 37.