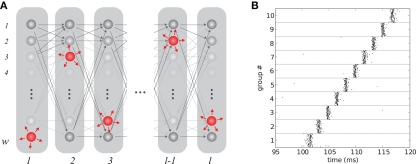
Figure 1.
A simple synfire chain. (A) Wiring diagram of a synfire chain. Excitatory neurons in each group (gray discs) have feed-forward connections to all neurons in the next group (gray arrows); in this version of the synfire chain model, inhibitory neurons in each group (red discs) project to random neurons in the entire network to create a global inhibition. (B) Synfire activity. If the first group is sufficiently stimulated, a volley of activity propagates through the chain. Each dot represents the spike time of a neuron; horizontal lines separate the spikes of consecutive neuron groups.