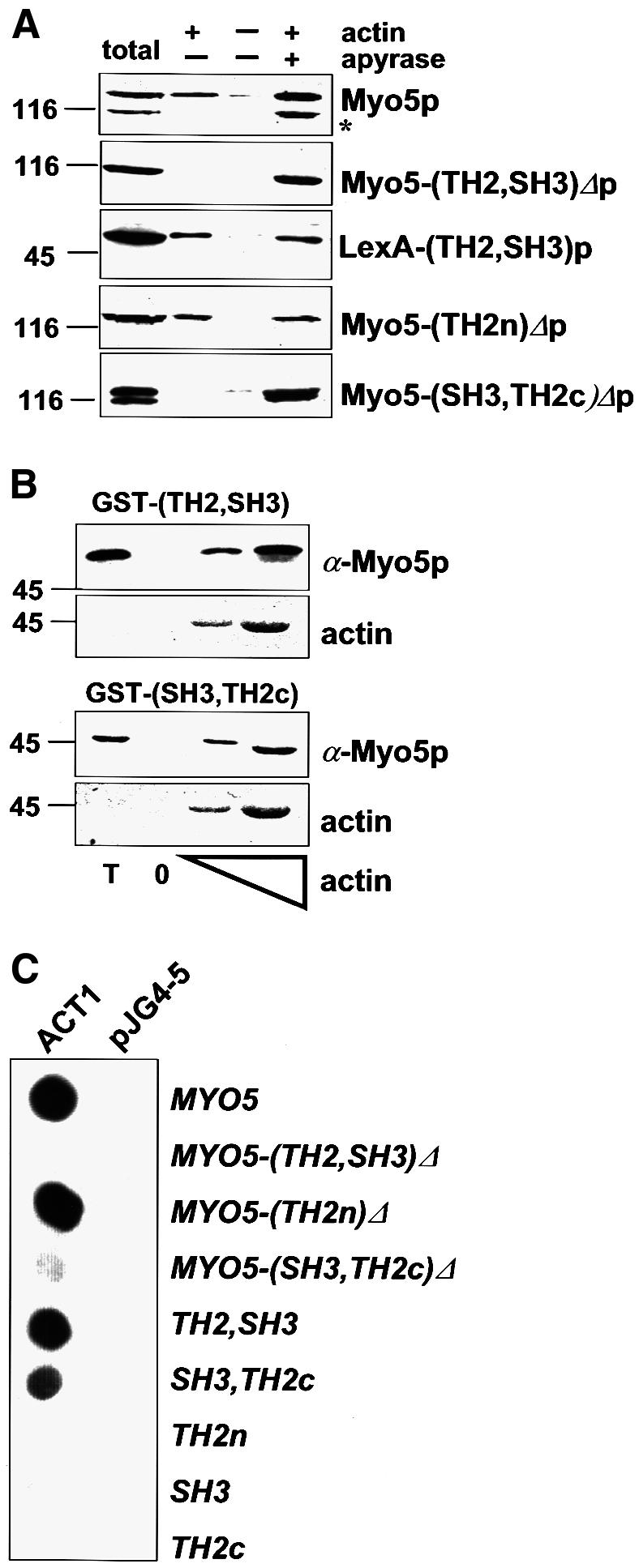
Fig. 1. The Myo5p tail interacts with actin. (A) Cytosolic fractions were prepared from strains bearing integrated versions of wt or mutant myo5 (SCMIG277, SCMIG278, SCMIG279, SCMIG280), or a strain expressing the TH2 and SH3 domains fused to LexA [EGY48 pEG202(TH2, SH3)] in a buffer containing 1 mM ATP. Purified actin (+ actin) or buffer (– actin) were added to the cell extracts. After allowing actin polymerization, one sample containing exogenously added actin was incubated with apyrase to hydrolyze ATP (+ apyrase). F-actin was recovered by centrifugation and the pellet analyzed by immunoblotting. 9E10 was used for detection of Myo5p, and EW/IK for detection of the LexA fusion protein. One quarter of the protein extract utilized per incubation was loaded as total. (B) Recombinant GST fusion proteins [GST–(TH2, SH3) or GST–(SH3, TH2c)] were incubated with cytosolic fractions of a wt strain (RH3975) and increasing concentrations of G-actin. After allowing actin polymerization, F-actin was recovered by centrifugation and the pellets were analyzed for the presence of the recombinant proteins by immunoblotting using the EW/IK antibody. The increasing amounts of actin in the pellet were monitored by Ponceau Red staining. The same amount of GST fusion proteins used per assay were loaded as total (T). (C) Different MYO5 tail fragments [pEG202MYO5, pEG202 myo5-(TH2, SH3)Δ, pEG202 myo5-(TH2n)Δ, pEG202 myo5-(SH3, TH2c)Δ, pEG202(TH2, SH3), pEG202(SH3, TH2c), pEG202(TH2n), pEG202(SH3), pEG202(TH2c)] were tested versus ACT1 (pJG4-5ACT1), or versus the B42 transcriptional activator (pJG4-5) as a control, in the two-hybrid assay on X-Gal-containing plates.
