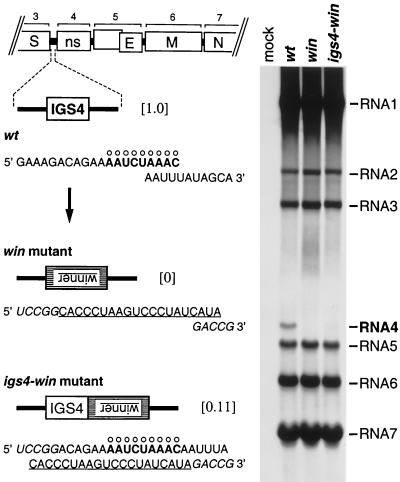
Figure 2.
Insertion of a high-affinity hnRNP A1 binding site in place of IGS4 or adjacent to IGS4. Left shows the sequences, in the positive sense, of the IGS4 regions of wild-type MHV (wt), the win mutant, and the igs4-win mutant. The consensus IGS motif is marked with ○, and the complement of the winner sequence is underlined. Residues derived from the BspEI and RsrII sites, used to construct the donor RNA transcription vectors for the mutants, are indicated in italics. The numbers in brackets are the relative levels of RNA4 synthesized by each virus. Right shows viral RNA metabolically labeled with [33P]orthophosphate, in the presence of actinomycin D, in 17Cl1 cells that were mock-infected or infected with wild-type MHV, the win mutant, or the igs4-win mutant. RNA was separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by fluorography.