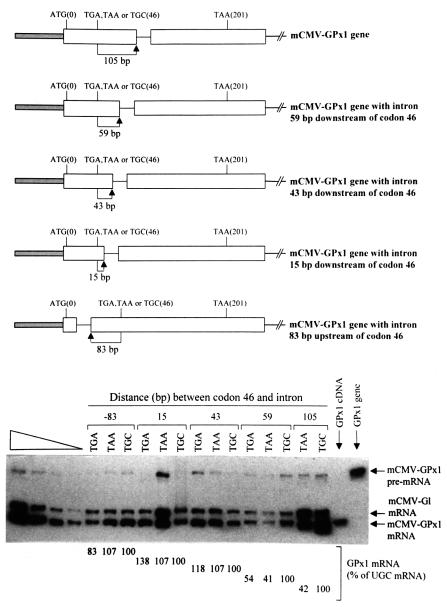
Fig. 1. Nonsense codons within the rat GPx1 gene elicit NMD when located ≥59 bp but not ≤43 bp upstream of the intron. Top: structures of the various GPx1 alleles, each of which is driven by the mCMV promoter. ATG(0) and TAA(201) specify the normal initiation and termination codons, and TGA, TAA or TGC(46) indicate the sequence at position 46, which is normally the Sec (TGA) codon. Bottom: RT–PCR analysis of the level of GPx1 mRNA as a function of intron position. NIH 3T3 cells were transiently transfected with the specified GPx1 test allele and the β-globin (Gl) reference allele. Total RNA was purified (Zhang et al., 1998b) and analyzed by RT–PCR as described (Moriarty et al., 1997, 1998). Notably, endogenous NIH 3T3 transcripts were not detected. For each intron position, which is specified as the distance in base pairs between codon 46 and the intron, the level of GPx1 mRNA was normalized to the level of Gl mRNA and is presented as a percentage of GPx1(UGC) mRNA, which was defined as 100. Results are the average of three independently performed experiments and did not differ by >8% except for the construct in which the TGA codon resided 15 bp upstream of the intron, where the maximum difference was 38% of the corresponding TGC construct. The left-most four lanes consist of serial dilutions of RNA, which were used to establish that there is a linear relationship between the amount of input RNA and the amount of each RT–PCR product. The right-most two lanes provide size standards for the products of GPx1 mRNA and GPx1 pre-mRNA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.