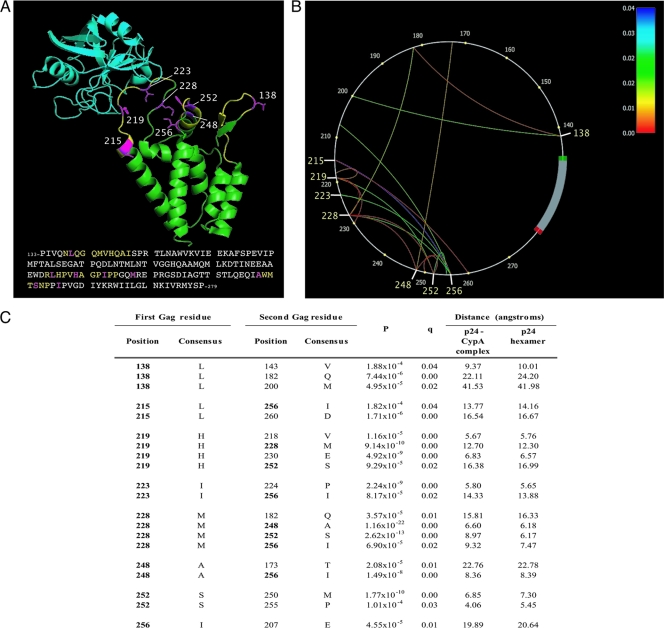
FIG. 2.
Location and covariation of high-variability amino acid residues in Gag p24 NTD. (A) Ribbon diagram of CypA (turquoise) bound to the HIV-1 Gag p24 NTD (green). The three loops are shown in yellow; eight high-variability residues, including H219, are shown in pink with side chains. Adapted from reference 12 (Protein Data Bank [PDB] code 1AK4). C-clade LANL consensus sequence is shown. (B) Phylogenetic dependency network for eight high-variability p24 residues (HXB2 positions 138, 215, 219, 223, 228, 248, 252, and 256) in 662 sequences from Durban, South Africa. Gag p24 is drawn counterclockwise, with the first NTD residue (HXB2 position 133) at the 3 o'clock position. Arcs indicate associations between amino acids (covariation). All associations are statistically significant (q < 0.05); the colors of the arcs correspond to q values. (C) Covariation of eight high-variability HLA-independent residues (in bold) with other Gag residues (for all covarying pairs, q was <0.05; P values are as shown). Consensus C-clade amino acid sequence derived from LANL (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov). Minimum distances between the carbon atoms (C-beta distance) of covarying residues in the folded p24 protein structure, determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, are shown. For any amino acid, C-alpha is the carbon atom next to the carbonyl group. In the side chain of an amino acid, the first carbon atom branching from C-alpha in the backbone is called C-beta; the C-beta distance is the distance between two C-beta atoms.