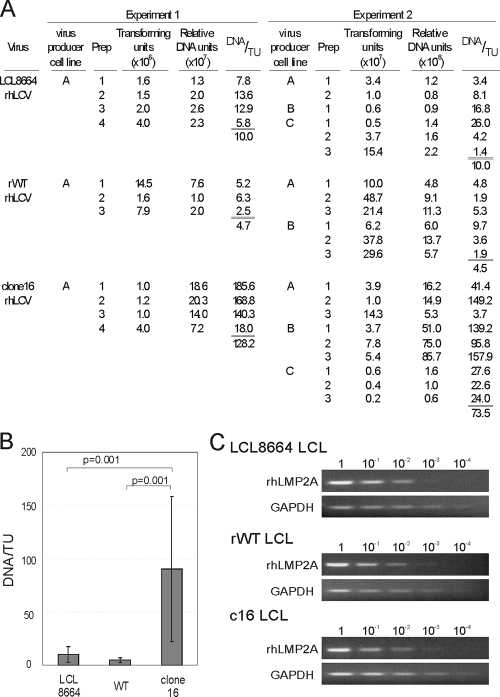
FIG. 4.
Comparison of B-cell-transforming activity by LCL8664, rWT, and clone 16 rhLCV. (A) Transforming activity in multiple virus preparations of LCL8664, rWT, and clone 16 rhLCV. Different virus-producing LCL infected with LCL8664 (lines A, B, and C), rWTrhLCV (lines A and B), and clone 16 rhLCV (lines A, B, and C) were used to make multiple virus preparations. Transforming activity (DNA/TU) was evaluated by calculating the number of relative viral DNA units required per transforming unit (TU). Virus preparations were PCR amplified together in two separate experiments, and the relative DNA units were normalized so that the transforming activity of the naturally occurring LCL8664 rhLCV was 10 DNA units/TU. (B) The efficiency of transforming activity (DNA/TU) for all virus preparations in experiments 1 and 2 is graphed. The overall average DNA/TU for LCL8664 rhLCV was 10.0 (n = 10), 4.6 for rWT rhLCV (n = 9), and 90.3 for clone 16 rhLCV (n = 13). P values (t test) less than 0.05 are shown. (C) rhLMP2A mRNA expression in LCL8664-, rWT-, and clone 16 rhLCV-infected LCL. Total RNA from LCL was reverse transcribed with gene-specific primers, and 10-fold serial dilutions (1 to 10−4) of cDNA were PCR amplified for rhLMP2A or GAPDH.