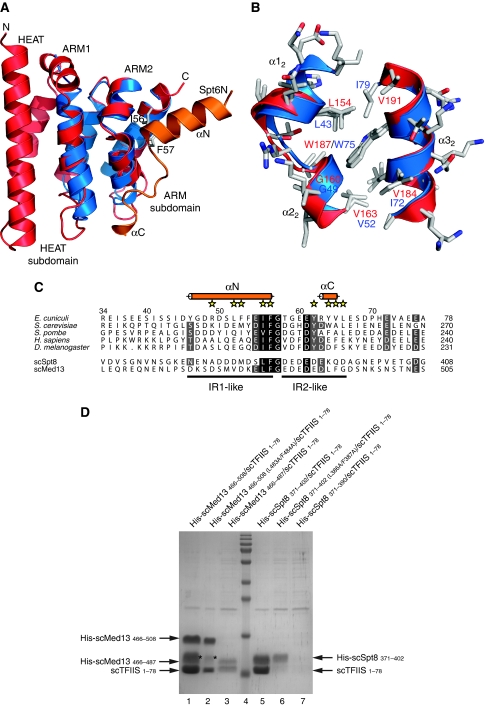
Figure 6.
Specific interaction of TFIIS N-terminal domain with Spt8 and Med13. (A) Superposition of E. cuniculi Iws1 (red) and mouse TFIIS Domain I (blue) structures. For comparison, the position of Spt6N (orange) bound to Iws1 is shown. (B) Superposition of the hydrophobic (IF-binding) pockets of E. cuniculi Iws1 (red) and mouse TFIIS domain I (blue). All side chains are shown. (C) Multiple sequence alignment of the Iws1-binding region of Spt6N (top five rows) and of the putative TFIIS-binding region of S. cerevisiae (sc) Spt8 and Med13 (bottom two rows). (D) Reconstitution by co-expression of the complexes formed between S. cerevisiae TFIIS (1–78) and Med13 (466–508), and S. cerevisiae TFIIS (1–78) and Spt8 (371–402). Importance of the IF motifs and acidic regions on complex formation is addressed by using specific mutants. Degradation products of Med13 are labelled with an ‘*'.