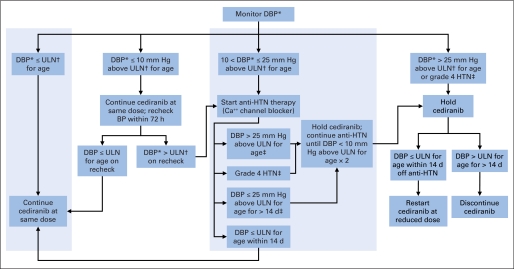
Fig A1.
Algorithm for management of hypertension in children and adolescents. Diastolic hypertension (HTN) was defined using age- and sex-specific normal values. Children and adolescents with baseline HTN or those receiving antihypertensive medication were excluded. Single-agent antihypertensive medication (central shaded region) could be used to control mild asymptomatic HTN (diastolic blood pressure [DBP] > 10 and ≤ 25 mmHg above normal) without modification of the cediranib dose. (*) Elevated DBP measurements were repeated twice to confirm the elevation. (†) Upper limit of normal (ULN) was defined as a DBP at the 95th percentile from age- and sex-appropriate normal values. (‡) If DBP > 25 mm Hg above ULN for age (verified) or grade 4 HTN occurred at any time, cediranib was held. Antihypertensive agents were used to control HTN as clinically indicated after cediranib was held. Calcium channel blockers (amlodipine or nifedipine) were recommended for cediranib-related HTN.