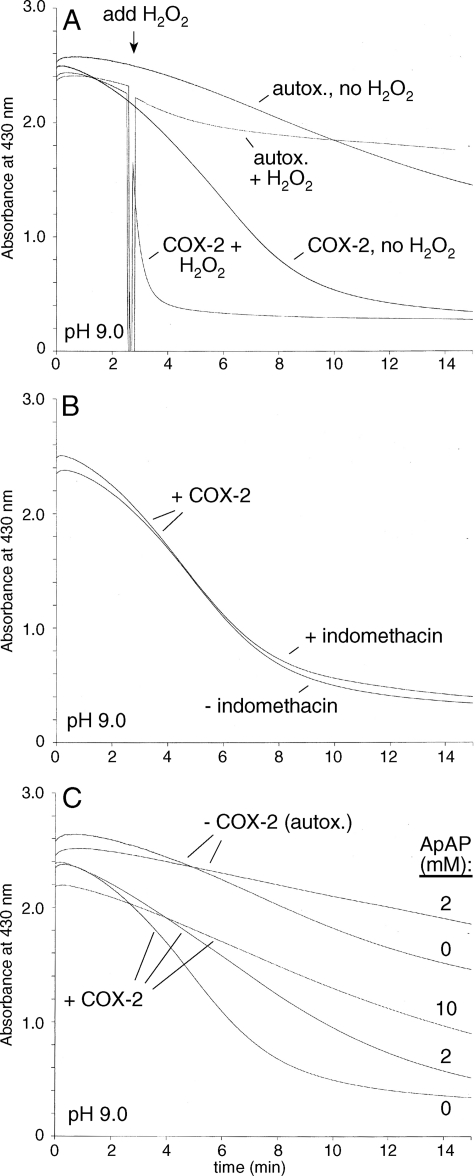
FIGURE 6.
Spectrophotometric analysis of the COX-2-catalyzed transformation of curcumin. A, transformation of curcumin was accelerated by the presence of 50 nm COX-2 compared with autoxidation. Addition of 300 μm H2O2 further accelerated the rate of COX-2-catalyzed transformation whereas it had only a small effect on autoxidation. B, addition of 10 μm indomethacin did not change the rate of COX-2 (50 nm) catalyzed transformation of curcumin. C, addition of acetaminophen (ApAP) dose-dependently inhibited the COX-2 (50 nm) catalyzed transformation of curcumin. All reactions were conducted using 100 μm curcumin and 1 μm hematin in 100 mm potassium phosphate buffer pH 9 in the absence or presence of 50 nm COX-2 as indicated. The absorbance at 430 nm was recorded in the time-drive mode using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer.