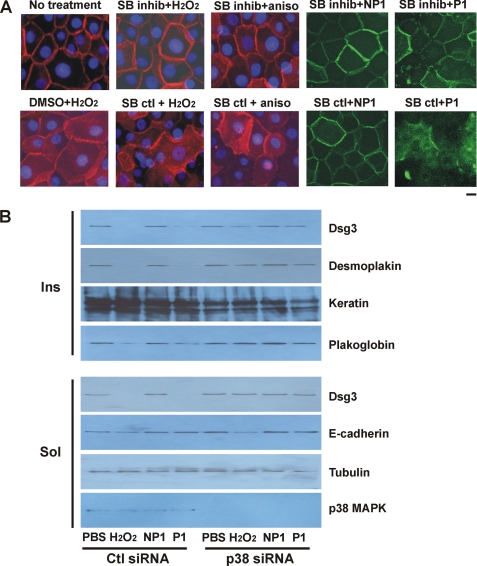
FIGURE 4.
Inhibition of p38 MAPK prevents Dsg3 endocytosis and depletion from desmosomal fractions. A, p38 inhibition decreases internalization of Dsg3 by p38 activators and pathogenic PV mAbs. PHEK were pretreated with 2 μm SB202190 (p38 inhibitor (inhib)) or SB202474 (an inactive analog control) or the same volume of Me2SO vehicle for 1 h, followed by 100 μg/ml anisomycin (aniso), 200 μm H2O2, or eGFP-conjugated nonpathogenic (NP1) or pathogenic (P1) PV mAb (200 μg/ml) for 4 h in medium containing 1.2 mm calcium. Subcellular localization of Dsg3 (red) or PV mAbs (green) was determined by immunofluorescence microscopy. p38 inhibition decreased the loss of cell surface Dsg3 caused by p38 activation and pathogenic PV mAbs. Scale bar = 10 μm. B, silencing of p38 MAPK expression prevents depletion of Dsg3 by oxidative stress or pathogenic PV mAb. PHEK were transiently transfected with siRNA specifically targeting p38 or a control (Ctl) siRNA for 48 h. Cells were treated with 200 μg/ml PV mAbs or 200 μm H2O2 for 4 h and lysed with buffer containing 1% Triton X-100. Protein levels in the Triton X-100-insoluble (Ins) and Triton X-100-soluble (Sol) fractions were determined by immunoblotting using specific antibodies as indicated. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments.