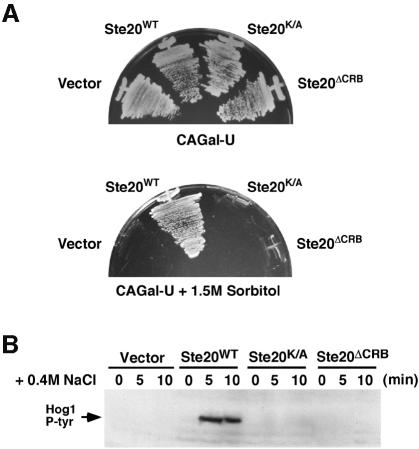
Fig. 8. Both the kinase activity and the CRIB domain of Ste20 are required for the osmotic stress response mediated by the SHO1 branch of the HOG pathway. (A) Strain DR76 (ssk2Δ ssk22Δ ste20Δ) was transformed with a multicopy (2 µm) plasmid containing either wild-type STE20, the kinase inactive STE20K/A allele or the STE20ΔCRB mutant allele lacking the Cdc42-binding domain. Transformants were streaked onto selective media containing galactose as the sole carbon source in the absence (upper panel) or presence (lower panel) of 1.5 M sorbitol. Whereas wild-type STE20 could rescue the osmosensitivity of the ste20Δ strain DR76, both mutant alleles of STE20 and the high copy-number expression vector alone failed to suppress the osmosensitive phenotype. (B) Activation of the Hog1 MAP kinase by osmotic stress in the transformants detailed in (A) was determined by immunoblot analysis using the 4G10 anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Exponentially growing cultures were harvested before (0), or at the indicated times after, the addition of 0.4 M NaCl, and subjected to immunoblot analysis.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.