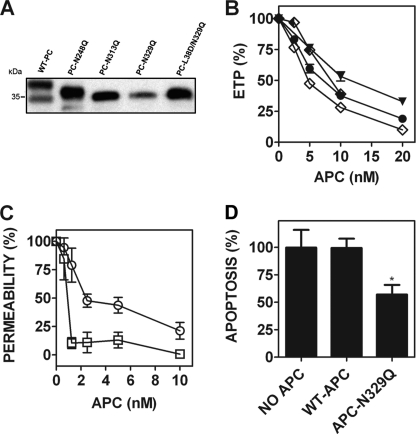
FIGURE 3.
Glutamine substitution of the N-linked glycan attachment site at Asn-329 causes enhanced endothelial barrier-protective and anti-apoptotic APC activity. A, each recombinant protein C (wild type protein C, PC-N248Q, PC-N313Q, PC-N329Q, and PC-L38D/N329Q) was reduced using β-mercaptoethanol and assessed by 7.5% SDS-PAGE analysis. The protein C heavy chain was subsequently detected by Western blot using a sheep anti-protein C polyclonal antibody. B, the anticoagulant activity of each APC variant was determined by a thrombin generation assay in protein C-deficient plasma (●, wild type APC; ▼, APC-N248Q; ♦, APC-N313Q; ♢, APC-N329Q; all 1.25–20 nm, except APC-N313Q, 1.25–10 nm). C, the endothelial barrier-protective properties of wild type APC (○) and APC-N329Q (□; 1.25–10 nm) were determined as described previously. D, endothelial cell pro/anti-apoptotic gene expression in the presence of wild type APC and APC-N329Q (both 5 nm) was measured by RT-PCR quantification of the relative expression of Bax/Bcl-2 mRNA transcripts, as described under ”Experimental Procedures.“ *, p < 0.05.