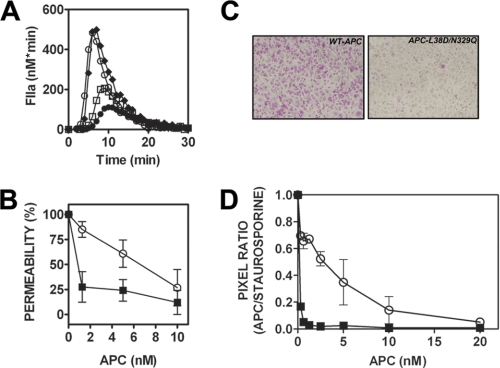
FIGURE 6.
APC-L38D/N329Q possesses no anticoagulant activity in plasma but demonstrates enhanced cytoprotective PAR-1 signaling. A, thrombin generation in protein C-deficient plasma was assessed in the presence of wild type APC and APC-L38D/N329Q. Thrombin generation (nm × min) was initiated with platelet-poor plasma reagent and CaCl2 as before, and the percentage of ETP (thrombin generation in the absence of APC) was determined. (○, no APC; □, 5 nm wild type APC; ●, 10 nm wild type APC; ♦, 20 nm APC-L38D/N329Q). B, EPCR-PAR1-dependent endothelial cell barrier protection by APC-L38D/N329Q is more potent than wild type APC. Barrier permeability assays using EA.hy926 cells were performed in the presence of wild type APC (○) or APC-L38D/N329Q (■; 1.25–10 nm) prior to thrombin treatment. Permeability is expressed as a percentage of total thrombin-induced endothelial cell barrier permeability. C, endothelial cell apoptosis was measured by accumulation of apoptosis-specific dye (pink-purple) in staurosporine-treated EA.hy926 cells following incubation with wild type APC or APC-L38D/N329Q (1.25 nm). D, APC concentration-dependent reduction in endothelial cell apoptosis (○, wild type APC; ■, APC-L38D/N329Q; 0.3125–20 nm).