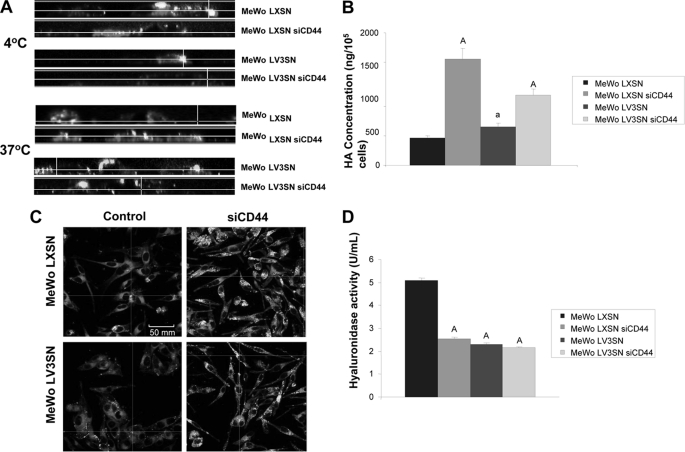
FIGURE 4.
Effect of CD44 silencing on hyaluronan catabolism of MeWo melanoma cells expressing or not the V3 isoform of versican. A, CD44 silencing causes a decrease in cell-surface binding and internalization of a FITC-HA complex in MeWo LXSN and MeWo LV3SN cells. Subconfluent cultures were treated overnight with hyaluronidase and incubated with FITC-HA for 1 h at 4 °C or 6 h at 37 °C. A CellMaskTM staining was used to visualize cell membrane. Cells were fixed and visualized using a Leica TCS SP5 AOBS confocal microscope. Images were processed using IMARIS software. B, CD44 silencing increases HA content in the culture media of MeWo LXSN and MeWo LV3SN cells. Conditioned media from cells cultured in serum-free medium for 24 h were collected and digested with protease solution. HA was determined with an ELISA-like assay. A representative experiment out of three performed is shown. Small letters indicate p < 0.05 and capital letters indicate p < 0.01 (versus MeWo LXSN). C, CD44 silencing increases endogenous expression of hyaluronan in MeWo LXSN and MeWo LV3SN melanoma cells. Subconfluent cultures from LXSN and LV3SN MeWo melanoma cells were fixed and incubated with a hyaluronan-binding protein (HABP). Cells were incubated with a FITC-streptavidin complex, mounted in Vectashield and analyzed under a Leica TCS SP5 AOBS confocal microscope. D, CD44 silencing causes a decrease in MeWo LXSN hyaluronidase activity but does not cause an additional decrease in MeWo LV3SN melanoma cells. Cell protein extracts were incubated in plates coated with BSA-conjugated hyaluronan. The remaining HA was detected with b-HABP as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A representative experiment out of three performed is shown. Capital letters indicate p < 0.01 (versus MeWo LXSN). Values are mean ± S.D.