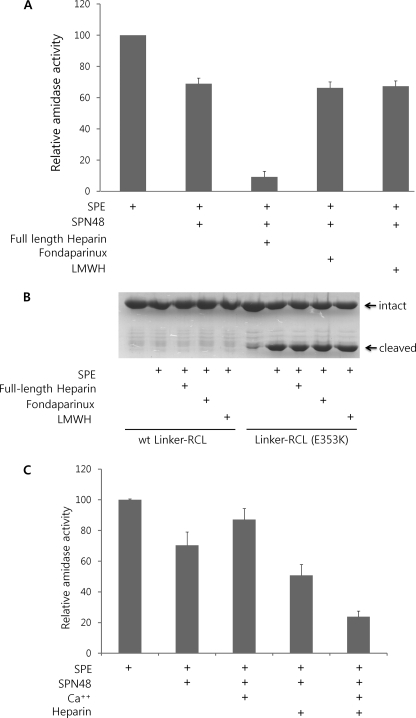
FIGURE 5.
Heparin and calcium effects on SPE inhibition by SPN48. A, heparin effect on SPE inhibition by SPN48 depending on the length of heparin. Full-length heparin accelerated the inhibitory activity of SPN48, whereas pentasaccharide unit of heparin (fondaparinux) and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH, ∼15-saccharide unit) did not affect SPN48 activity. SPE (300 ng), SPN48 (600 ng), full-length heparin (200 ng), fondaprinux (200 ng), or low molecular weight heparin (200 ng) were used in this experiment in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) containing 100 mm NaCl. Amidase activity of SPE was measured after 2 h of incubation at 30 °C. B, heparin does not affect the proteolytic activity of SPE. Both full-length heparin (200 ng), pentasaccharide heparins (fondaparinux; 200 ng), and low molecular weight heparin (200 ng) did not cause a marked change in the enzymatic activity of SPE. The wild-type and the mutant (E353K) Linker-RCL (25 μg each) were used as substrates for SPE (50 ng) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) containing 5 mm CaCl2. C, synergistic role of heparin and calcium ion on the inhibition of SPE by SPN48. The amidase activity of SPE was measured using the fluorescent peptide after 1 h of incubation at 30 °C. SPE (300 ng), SPN48 (600 ng), 5 mm CaCl2, and/or full-length heparin (200 ng) were used in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5).