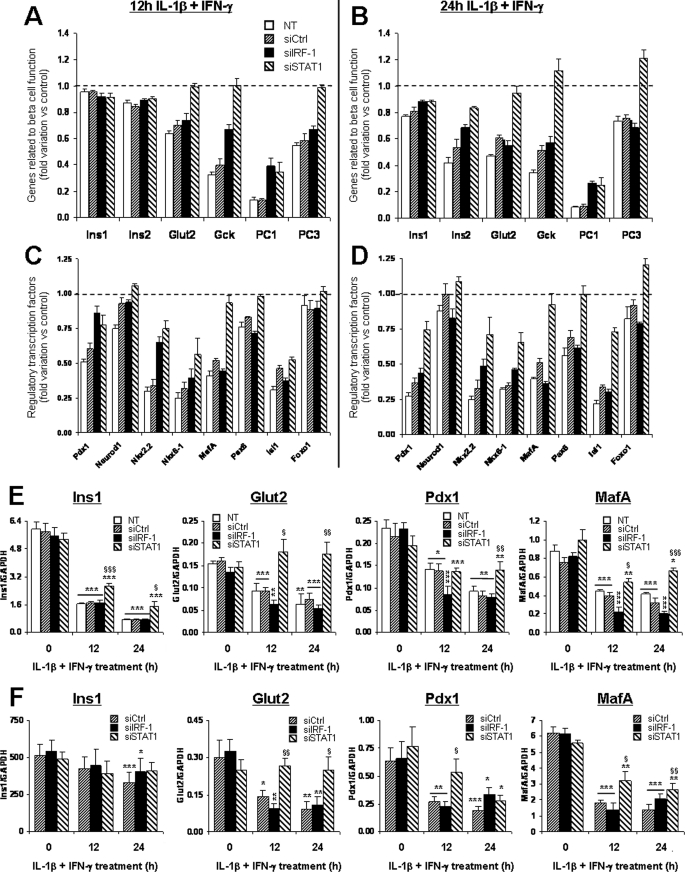
FIGURE 3.
STAT1 silencing partially prevents cytokine-induced down-regulation of genes involved in β-cell differentiation and function. INS-1E cells (A–E) or primary FACS-purified rat β-cells (F) were left untransfected (NT) or transfected with 30 nm of si-control, siIRF-1, or siSTAT1. After 24 h of recovery post-transfection, cells were left untreated or exposed to 10 units/ml IL-1β and 100 units/ml IFN-γ for 2, 12, or 24 h as indicated. Expression of genes related to β-cell function (A and B) or regulatory transcription factors (C and D) were analyzed by microarray. Results represent the mean fold variations ± S.E. of the genes as compared with untreated controls after 12 h (A and C) or 24 h (B and D) of cytokine treatment (n = 3). Statistical analyses for the represented genes are described in supplemental Table 1. E, independent confirmation experiments in INS-1E cells Ins1, Glut2, Pdx1, and MafA mRNA expression were assayed by real-time RT-PCR and normalized for the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Results are mean ± S.E. of four independent experiments. F, confirmation experiments in primary rat β-cells. Ins1, Glut2, Pdx1, and MafA mRNA expression was assayed by real-time RT-PCR and normalized for the housekeeping gene GAPDH. Results are mean ± S.E. of five independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001 versus untreated (i.e. not treated with cytokines) or untreated transfected with the same siRNA. §, p < 0.05; §§, p < 0.01; and §§§, p < 0.001 versus untransfected and si-control treated with cytokines at the same time point, ANOVA followed by Student's t test with Bonferroni correction.