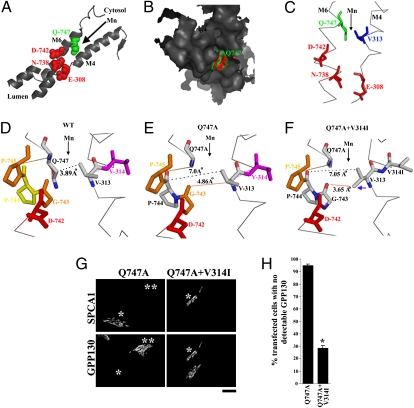
Fig. 3.
The Q747A substitution increases the size of the SPCA1 ion permeation cavity. (A–C) SPCA1-WT was modeled using the MODBASE server as described in Materials and Methods. The M4 and M6 transmembrane domains are depicted in cartoon (A), surface (B), and ribbon (C) forms using the open source PyMol software. Ion-binding residues, E308, N738, and D742 are depicted in red; residue Q747 is in green; and V313 is in blue. Arrowheads indicate the path used by ions to reach the ion-binding site. (D–F). Distances across the ion permeation cavity are shown for the computed structures of SPCA1-WT, SPCA1-Q747A, and SPCA1-Q747A+V314I. Distances between M4 and M6 were measured using the “Measurement Wizard” in PyMol and the structures of the SPCA1 mutants were obtained using the “Mutagenesis Wizard” of PyMol. Blue arrowhead in F shows the rotation of the side chain of V313 after the V314I substitution. Black arrowheads indicate the likely path traversed by ions en route to the ion-binding site. (G) HeLa cells were transfected with HA-SPCA1-Q747A or HA-SPCA1-Q747A+V314I and imaged 24 h later to detect GPP130 and HA. GPP130 was degraded in cells transfected with SPCA1-Q747A but not in those expressing the V314I mutation (single asterisk). Untransfected cells in the SPCA1-Q747A transfected culture exhibited Golgi-localized GPP130 (double asterisk). (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (H) Quantitation of percentage of transfected cells lacking detectable GPP130 from G above (mean ± SE, n = 50 cells from four independent experiments, P < 0.05).