Fig. 2.
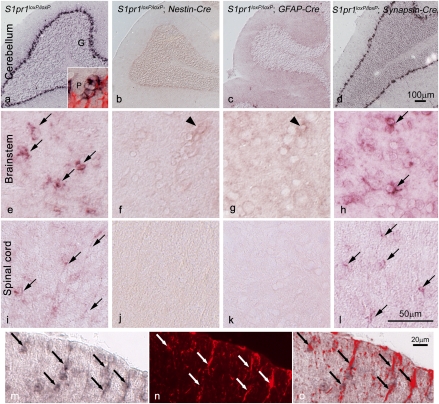
S1P1 gene expression and Cre-mediated conditional loss as detected by in situ hybridization identify astrocytes in the CNS. In situ hybridization shows S1pr1 expression (dark label) throughout the adult CNS (shown for cerebellum, brainstem, and spinal cord) in WT mice (A, E, and I) that is lost after conditional deletion in S1pr1loxP/loxP; Nestin-Cre (B, F, and J) and S1pr1loxP/loxP; GFAP-Cre (C, G, and K) mice but not in S1pr1loxP/loxP; Synapsin-Cre (D, H, and L) mice. In WT mice, S1pr1 message is abundant in the Bergmann glia of the Purkinje layer in the cerebellum (A), which was confirmed by double labeling with a GFAP antibody (A Inset, red; P, Purkinje neuron) and not observed in other neuronal populations (G, granule neurons). In brainstem (E–H) and the white matter of spinal cord (I–L), S1pr1 message is present (arrows) in WT (I) and S1pr1loxP/loxP; Synapsin-Cre (L) mice but is not detected when conditionally deleted in Nestin-Cre (J) or GFAP-Cre (K) cells. Labeling is occasionally observed in presumptive endothelial cells (arrowheads). (M–O) Double-labeling cells using S1pr1 in situ hybridization, combined with GFAP immunolabeling, confirms S1pr1 expression in spinal cord astrocytes. In situ hybridization (M, dark label), GFAP immunolabeling (N, red), and merged image (O). (Scale bars: A–D, 100 μm; E–L, 50 μm; M–O, 20 μm.)