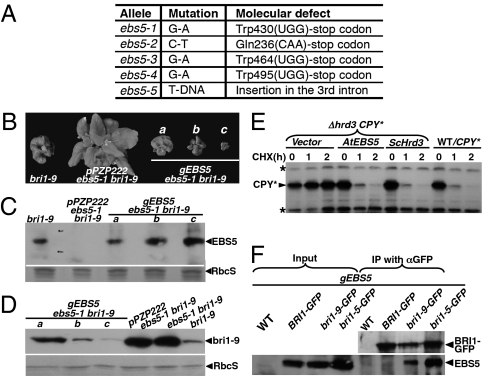
Fig. 3.
EBS5 encodes the Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast Hrd3/mammalian Sel1L protein. (A) Identified nucleotide change and predicted molecular defects of five ebs5 alleles. (B) Shown here are pictures of bri1-9 and four transgenic ebs5-1 bri1-9 lines carrying the pPZP222 vector or a genomic EBS5 transgene. (C) Immunoblot analysis of EBS5 abundance in 2-wk-old seedlings of bri1-9 and 4 transgenic ebs5-1 bri1-9 lines shown in B. (D) Immunoblot analysis of the bri1-9 abundance in 2-wk-old seedlings of bri1-9, ebs5-1 bri1-9, and four ebs5-1 bri1-9 transgenic lines shown in B. For C and D, equal amounts of total proteins extracted from 2-wk-old seedlings were separated by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-EBS5 (C) or anti-BRI1 (D). Coomassie blue staining of a duplicate gel showing the relative amount of RbcS served as loading control. (E) Immunoblot analysis of the CPY* abundance in the wild-type yeast cells transformed with a CPY* plasmid or the yeast Δhrd3 CPY* strain transformed with the indicated plasmid. Equal amounts of total proteins extracted from yeast cells of midlog growth phase treated with or without CHX were separated by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. Asterisk indicates two cross-reacting bands used for loading control. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of bri1-5/bri1-9 with EBS5. Equal amounts of total proteins and anti-GFP immunoprecipitates from control/coinfiltrated tobacco leaves were separated by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP or anti-EBS5 antibodies.