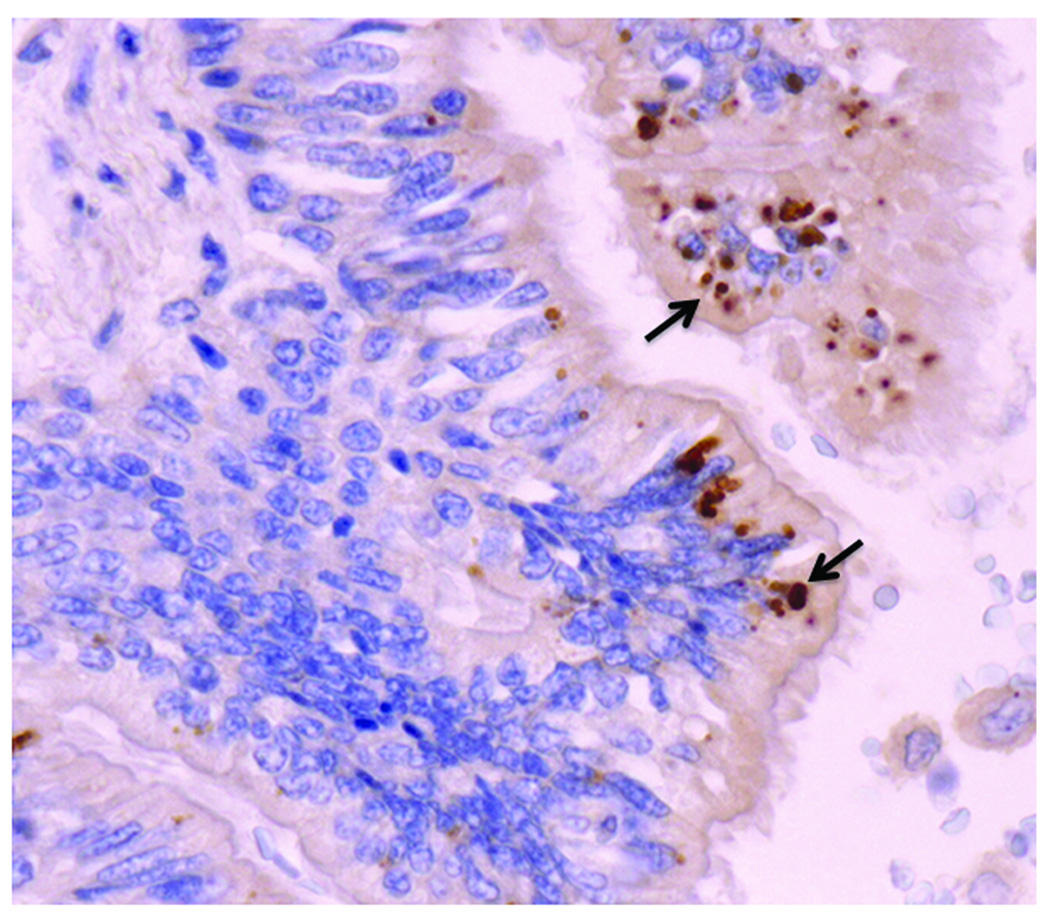
Figure 1.
Intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (ICI, arrows, in brown) in ciliated bronchial epithelium of an infant with acute fatal Kawasaki Disease, detected by immunohistochemistry using KD synthetic antibody. Nuclei stain blue with the hematoxylin counterstain. The ICI are consistent with aggregates of viral protein and RNA, and are likely the result of infection with a “new” RNA virus.