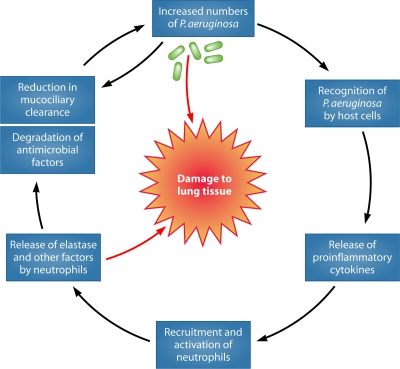
FIG. 2.
Cycle by which the presence of P. aeruginosa bacteria in the airways of individuals with CF leads to progressive pulmonary injury. In addition to directly damaging lung tissues, P. aeruginosa expresses factors that are recognized by the host immune system, resulting in release of proinflammatory cytokines. These cytokines cause the recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils that upon activation release elastase, collagenase, and oxygen radicals. The result is pulmonary injury as well as impaired bacterial clearance, which in turn leads to increased numbers of bacteria and exacerbation of the cycle.