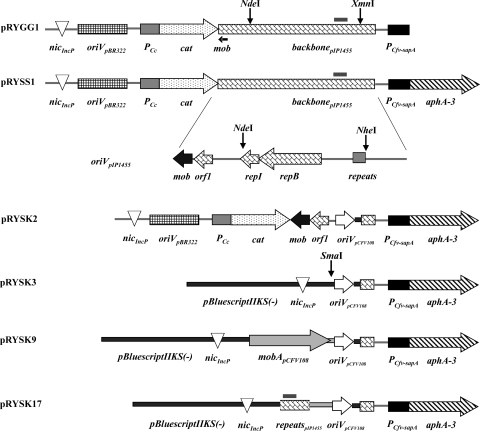
FIG. 2.
Constructions defining requirements for plasmid mobilization by the C. fetus subsp. venerealis T4SS. C. fetus cannot be readily transformed; thus, all vectors carry a P-type nic site to introduce the plasmid to donor cells. Selection in Campylobacter relies on a kanamycin resistance cassette (aphA-3) expressed from the C. fetus sapA promoter. Regions of the C. coli plasmid pIP1455 (backbone) are shown with functional modules identified in the expanded view below, including a putative mob gene (mob) and a potential P-type nic site (repeats). The C. fetus replicon (oriVpCFV108) and putative relaxase gene mobA from pCFV108 (gray arrow) are shown.