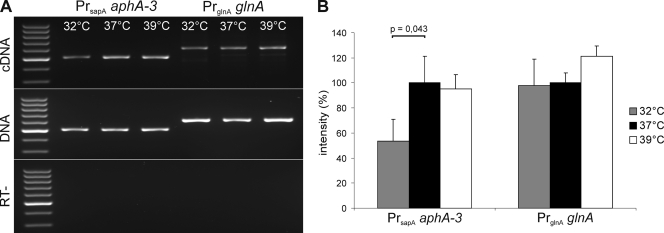
FIG. 4.
Expression of aphA-3 controlled by PrsapA is significantly reduced at 32°C. (A) RNA of Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis ATCC 19438(pRYSS1) was isolated after cultivation at the temperatures shown. cDNA of aphA-3 and glnA was produced with reverse transcriptase (RT) from an equivalent portion of total RNA and amplified, and the products were analyzed on a 2% agarose TAE gel (upper panel). Plasmid DNA (aphA-3) and genomic DNA (glnA) templates served as positive controls for the amplification conditions (middle panel). Negative controls for DNA contamination (RT−) lacked reverse transcriptase (lower panel). (B) The intensities of products of amplified cDNAs were measured with ImageJ 1.43 (http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/), and the yield for each gene is expressed relative to the value obtained after cultivation at 37°C. Significantly lower expression of the aphA-3 marker controlled by PrsapA was measured at 32°C compared to 37°C growth, as indicated (unpaired t test). Standard deviations from three independent experiments at each growth temperature are shown.