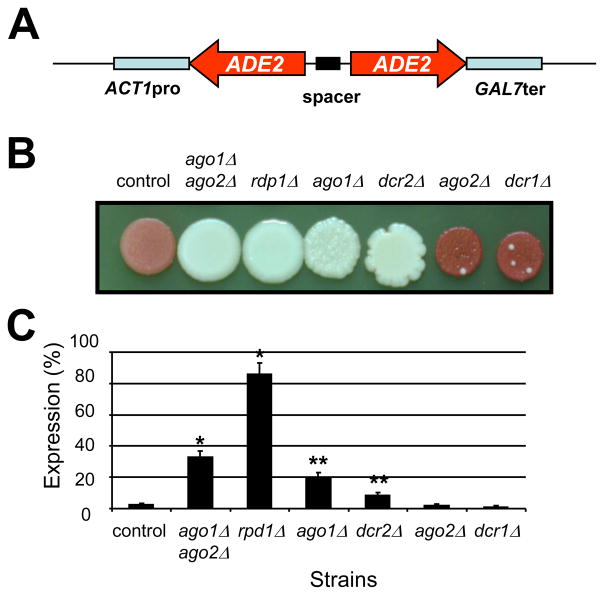
Fig. 1.
The role of the argonaute-, RdRP-, and Dicer-like genes in the RNA interference process of C. neoformans. (A) Map of the pRNAi plasmid used to transform C. neoformans. (B) Coloration of the different mutant strains after 4 days on YPD agar medium at 30°C. (C) ADE2-specific mRNA levels as measured by quantitative RT-PCR. An ade2 knockdown strain was constructed by integration of the pRNAi plasmid (GeneBank HM352736, kindly given by T. Doering) in its genome. This strain (control, strain name) produced red colonies on complete medium and the levels of ADE2-specific mRNA were fiftyfold lower in the control strain than in the WT strain. To test the importance of each putative RNAi-component on the silencing of ADE2, the control ADE2-knockdown strain was crossed with different single and double RNAi mutant strains. As shown here, RDP1 was the only gene completely necessary for ADE2-silencing. AGO1 and DCR2 also play a major role whereas the deletion of either DCR1 or AGO2 appeared to have a very limited impact on silencing. * Student t-test P value <0.001.** Student t-test P value<0.05