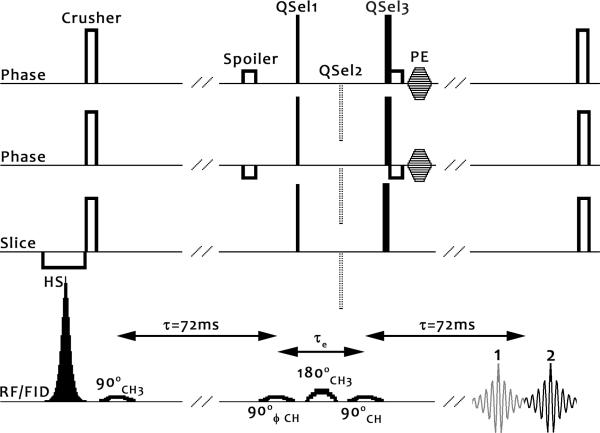
Figure 1. The Hadamard-SelMQC pulse sequence diagram.
Frequency-modulated hyperbolic secant (HS) inversion pulses, described later in the text, are used for Hadamard style slice encoding. A crusher removes any incompletely inverted magnetization. An initial 90° 1.3ppm (CH3) frequency selective Gaussian pulse excites lipid and lactate. After an evolution period τ=1/2J of 72 ms (41), the anti-phase magnetization is split into DQ and ZQ coherences by a 90° frequency selective Gaussian applied at 4.1ppm (CH). Phase cycling was best accomplished in our experience by cycling this RF pulse, and it has been designated with a ϕ symbol.
Choice of quantum selection gradients (QSel) during the evolution period, τe, determines the final observed quantum coherence pathway. Minimization of this evolution time reduces J-coupling modulation and diffusion based signal loss. The QSel gradient moment ratios (1:0:2) in the solid lines correspond to selection of one double quantum coherence pathway (termed DQ→ZQ), observed as echo #2, and this is the echo pathway we have chosen in this study. An alternate choice is the other double quantum coherence pathway (ZQ→DQ, QSel moments of 0:−1:2) which generates echo #1. We chose DQ→ZQ because the entire echo is typically included in the receiver time window, though both pathways were observed to provide almost identical sensitivity. Both options provide very high levels of fat suppression, as the lipid experiences a spin-echo sequence with unbalanced gradients.
Another choice is to refocus all coherences (DQ→DQ, QSel moments 1:−1:2), and obtain both echo #1 and #2. In this case a non-selective 180 hard pulse should be employed to minimize the evolution time. However, both lipid and lactate signals are obtained since the gradients are no longer unbalanced for lipid, leading to full lipid signal in a single acquisition. Still, if the ϕ pulse is cycled in combination with the receiver, averaging of two cycled acquisitions eliminates lipid signal, leaving lactate. Given the large lipid-to-lactate ratios in lipid-rich areas, this technique is highly susceptible to motion effects and very minor scanner instabilities. It also doubles the required acquisition time.