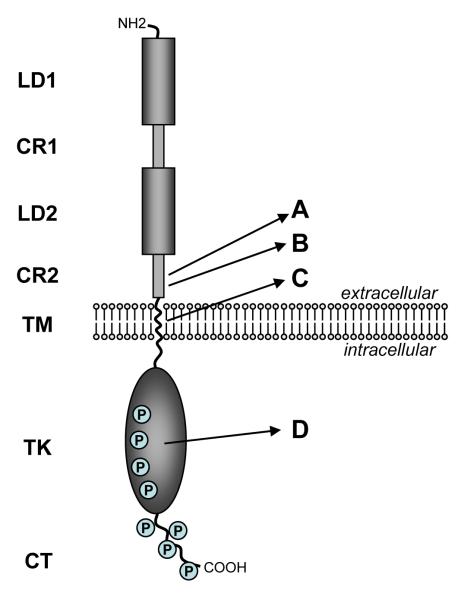
Figure 1.
Structure of the HER2 and Neu proteins. The domain structure is shown on the left consisting of two ligand binding regions (LD1 & LD2), two cysteine-rich regions (CR1 & CR2), a short transmembrane domain (TM), a catalytic tyrosine kinase domain (TK), and a carboxy terminal tail (CT). Numerous sites of tyrosine phosphorylation wiithin the TK and CT domains are indicated by circled P.The letters on the right point to specific areas that are altered or mutated in certain naturally occuring or experimentally induced cancers discussed in the text. A) site of somatic mutations found in tumors arising in MMTV-neu mice. B) site of the 48bp deletion in the naturally occuring human ΔHER2 isoform. C) site of the mutation in the neuT oncogene initially discovered in a rat carcinogen induced tumor model and subsequently used in numerous in vitro and transgenic experimental models. D) site of mutations found in rare cases of human lung cancers.