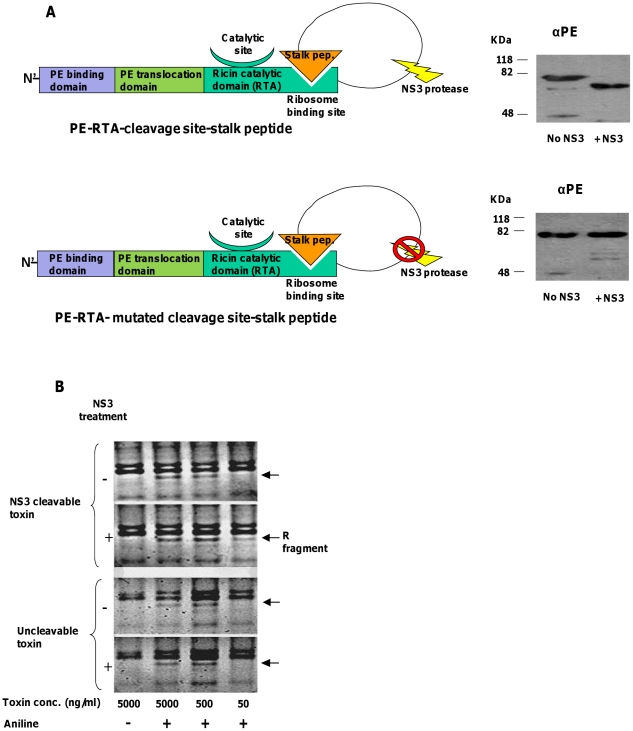
Figure 4. In-vitro cleavage by NS3 and ribosome depurination assay of RTA-based zymoxins.
(A). Left panel: A schematic representation of the toxins “PE-RTA-cleavage site-stalk peptide” and “PE-RTA- mutated cleavage site-stalk peptide”. Right panel: in-vitro cleavage by NS3: 3000ng of each toxin were incubated with or without 1000ng of recombinant MBP-scNS3 fusion in a total volume of 60µl for 1 hour at 37°C. Afterwards, 250 ng of each toxin were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting by anti-PE (αPE) polyclonal antibodies. (B). Ribosome depurination assay: A serial dilution of each toxin (treated or untreated with NS3) was incubated with 10µl of rabbit reticulocyte lysate for 30 minutes at 30°C, after which total RNA from each mixture was extracted. Half of the RNA was treated with acidic aniline (1M aniline in 2.8 M acetic acid) for 10 minutes at 40°C and the other half remained untreated. Next, RNA was extracted and analyzed by 3% TBE agarose gel electrophoresis and staining with ethidium bromide. The position of the “R fragment”, which released from rRNA of ricin-treated ribosomes after treatment with aniline, is marked by an arrow.