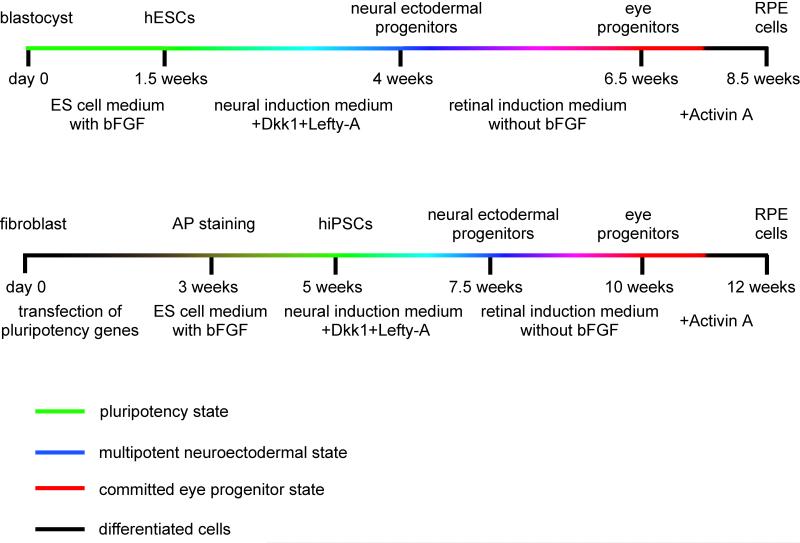
Figure 2.
Schematic diagrams of the differentiation protocols used to obtain retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells from ES or induced pluripotent stem cells. While the time periods required to obtain human ES cells and iPS cells differ by several weeks, the time to obtain RPE cells from them is similar. In a first step, neuroectodermal progenitors are generated from ES/iPS cells by exposing the cells to inhibitors of the WNT signaling pathway such as Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) or Nodal, and Lefty-A. In a second step, RPE cells are generated from neuroectodermal cells upon plating onto a laminin coated dish and culturing in a medium lacking FGF but containing activin A. Note that both neuroectodermal and RPE cells can be obtained from ES/iPS cells without the addition of Dkk1/Nodal or Activin A, but the efficiency of obtaining RPE cells under such conditions is much lower compared with conditions containing the respective factors.