Fig. 8. In vitro ubiquitination of HSP70 using E1-E2-E3 system and in vivo interaction of p62 with HSP70.
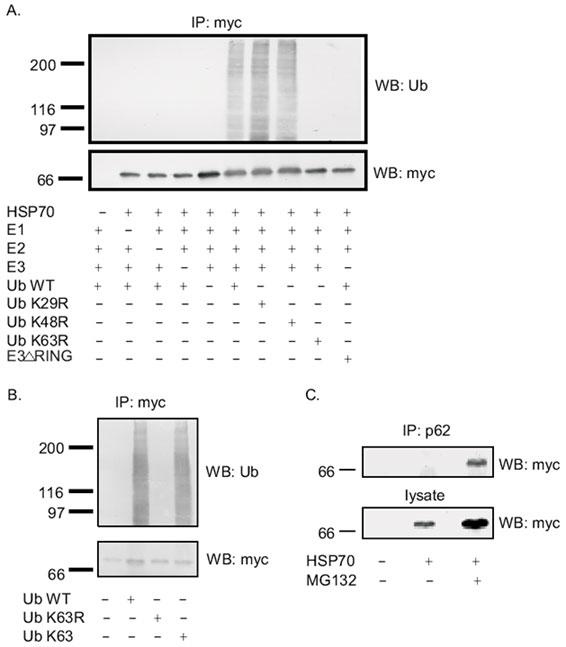
A: myc-tagged HSP70 protein expressed in HEK cells was immunoprecipitated by myc-polyclonal antibody and used as a source of substrate for in vitro ubiquitination +/- E1, E2, E3, WT-Ub, Ub K29R, Ub K48R, Ub K63R. The reactions were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and Western blotted with myc monoclonal antibody (bottom panel) to detect HSP70 or with ubiquitin monoclonal antibody (top panel) to detect ubiquitination. B: myc-tagged HSP70 protein expressed in HEK cells was immunoprecipitated by myc-polyclonal antibody and used as a source of substrate for in vitro ubiquitination in the absence or presence of wild type ubiquitin or Ub K63R or Ub K63. The reactions were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and Western blotted with myc monoclonal antibody (bottom panel) to detect HSP70 or with ubiquitin monoclonal antibody (top panel) to detect ubiquitination. C: In vivo interaction of HSP70 and p62. Transfection of myc-tagged HSP70 into HEK293 cells was performed and the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with p62 polyclonal antibody, followed by Western blot with anti-myc monoclonal antibody.
