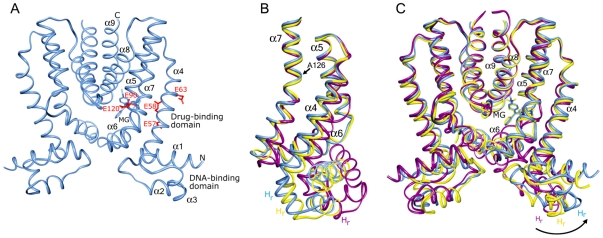
Figure 1. The conformational plasticity of QacR.
A) Structure of the wild type QacR-malachite green (MG) complex (space group P42212). QacR is shown as a light blue ribbon. The nine α helices, N- and C-termini, and DNA- and drug-binding domains are labelled. MG is shown as light blue sticks and the acidic residues of the multidrug-binding pocket, residues E57, E58, E63, E90, and E120, are shown as red sticks. B and C) Superimpositions of one subunit of wild type QacR bound to IR1 DNA (space group P65, magenta ribbon) and MG (space group P42212, blue ribbon), and QacR(E90Q) bound to MG (space group P62, yellow ribbon) highlighting the pendulum motion of helix α4 (B) and the bending and rotation of helix α7 originating at residue A126 (C) that lead to reorientation of the recognition helices (Hr) of the DNA-binding domain.