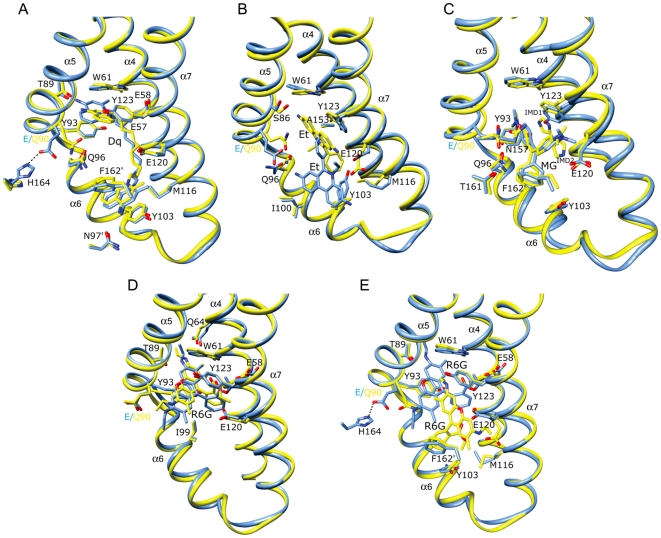
Figure 2. Multidrug binding by QacR(E90Q).
A - E) Superimpositions of the structures of the multidrug-binding pockets of wild type (wt) QacR-drug (light blue) and the corresponding QacR(E90Q)-drug (yellow) complexes. For clarity, only the side chains of QacR residues that are within 5 Å of (A) dequalinium (Dq), (B) ethidium (Et), (C) malachite green (MG), (D) rhodamine 6G (R6G) site 1, and (E) rhodamine 6G (R6G) site 2, are shown and labelled. Helices containing drug-interacting residues are labelled in black, and carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms are coloured light blue or yellow, blue and red, respectively. The salt bridge between QacR residues E90 and H164 in the wt QacR-Dq and wt-QacR R6G structures is shown as a dashed line in panels A and E. The imidazoles that are found in the drug-binding pocket of the QacR(E90Q)-MG complex are shown and labelled.