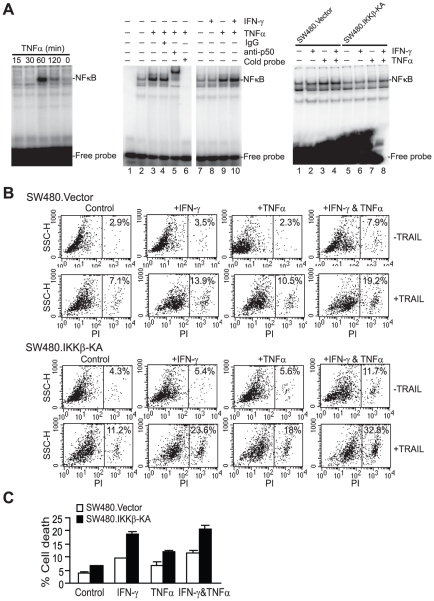
Figure 4. TNFα-mediated NF-κB activation on TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
A. Analysis of IKKβ-KA-mediated inhibition of NF-κB activation. Left panel: TNFα-induced NF-κB activation kinetics. SW480 cells were treated with TNFα for the indicated time. Nuclear extracts were prepared and used in the EMSA using a double-stranded oligo nucleotide probe containing NF-κB consensus sequence. Middle panel: specificity of NF-κB EMSA. SW480 cells were treated with IFN-γ, TNFα or both IFN-γ and TNFα for 60 min and analyzed for NF-κB activation by EMSA. IgG (lane 4), anti-p50 subunit of NF-κB antibody (lane 5), and excess molar ratio of cold probe (lane 6) were used for the specificity assay. Right panel: inhibition of NF-κB activation by IKKβ-KA mutant. SW480.Vector and SW480.IKKβ-KA cells were treated with IFN-γ, TNFα or both IFN-γ and TNFα for 60 min and used in the EMSA assay as shown above. B. Sensitivity of SW480.Vector and SW480.IKKβ-KA cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Tumor cells were treated with IFN-γ, TNFα, or both IFN-γ and TNFα overnight, followed by incubation with recombinant TRAIL for approximately 24 h. Cells were then stained with PI and analyzed for cell death. C. Quantification of TRAIL-induced cell death. Cell death as shown in B was quantified.