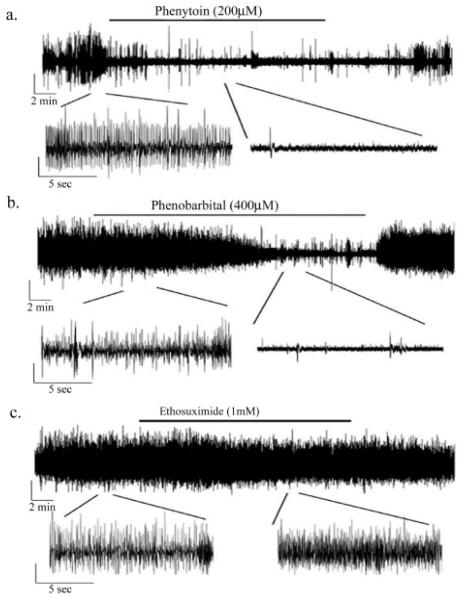
Figure 7.
Standard AEDs are effective at blocking seizure activity - Representative field potential recordings of the effect of standard anti-epileptic drugs on seizure activity in glutamate treated slices at DIV 30. A. Phenytoin (200μM) is effective at blocking seizure activity during a 20 minute perfusion and can be washed out. On average, phenytoin decreased field potential amplitude by 23.4 ± 9.3 % (P=0.045) and frequency by 83.8 ± 4.6% (p<0.001, n=4) B. Phenobarbital (400μM) is also effective at blocking seizure activity during the 20 minute period of perfusion, amplitude decreased by 23.3 ± 8.5% (p=0.035) and frequency decreased by 77.3 ± 12.7% (p<0.001) following 15 minutes of drug perfusion (n=4). C. Ethosuximide (1 mM), is not effective at blocking seizure activity in glutamate injured OHSCs (p>0.05, n=4). All vertical bars = 0.1mV