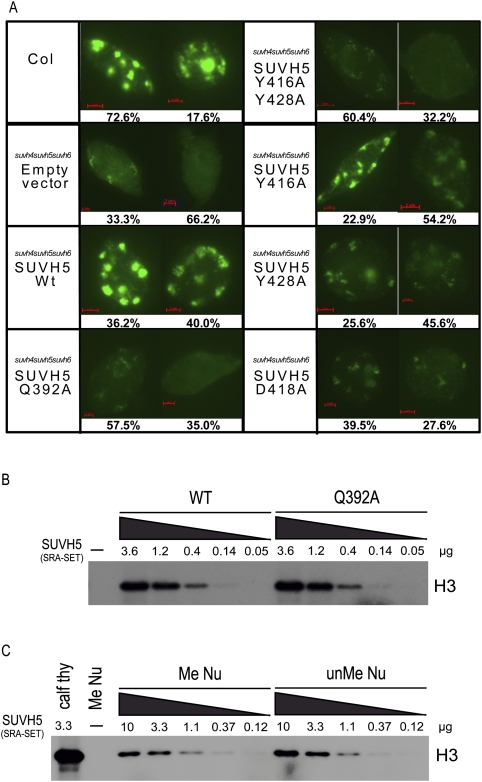
Figure 6.
Histone methylation analysis. (A, left) Immunofluorescence detection of H3K9 dimethylation in nuclei isolated from the indicated genotype. Images representing the two most predominant classes of nuclei are shown, and percentages out of 200 nuclei are indicated below. See Supplemental Figure 6 for a full breakdown of classes and percentages for each mutant. (B) HMTase assays using a wild-type or a Q392A mutant SUVH5 SRA-SET protein (amino acids 362–794) and calf thymus histones as a substrate. 3H-radiolabeled SAM was supplied as the methyl donor. The concentration of SUVH5 protein used for each assay is indicated in micrograms, and the position of histone 3 (H3) is indicated (at the right). (C) HMTase assays using a wild-type SUVH5 SRA-SET protein (amino acids 362–794) and either calf thymus histones (Calf thy) or mononucleosomes assembled using methylated (Me Nu) or unmethylated (unMe Nu) DNA. The concentration of SUVH5 protein used for each assay is indicated in micrograms, and the position of histone 3 (H3) is indicated (at the right).