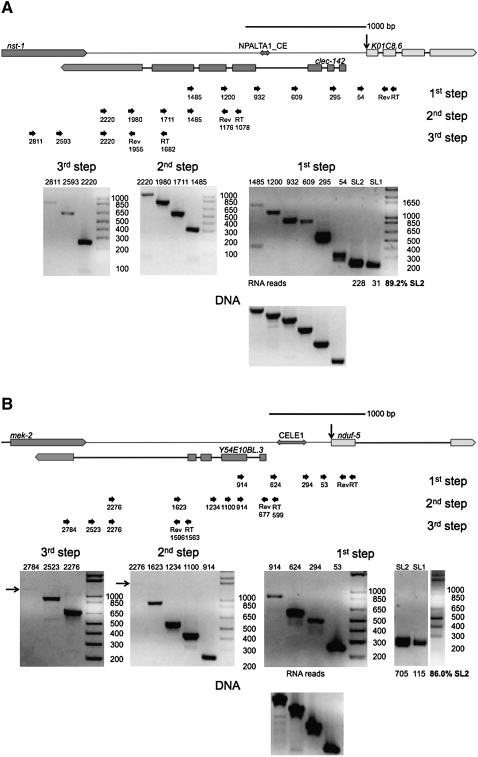
FIGURE 3.
Detection of RNA along the entire region upstream of SL2 trans-spliced genes. (A) The genomic arrangement of K01C8.6 is depicted above. This gene is ∼2.1 kb downstream from nst-1. The gene clec-142 lies on the opposite strand between these two genes. The transposon NPALTA1_CE is indicated as a double arrow upstream of K01C8.6. Gels of overlapping RT-PCRs indicate that RNA is transcribed along the entire region between K01C8.6 and the nearest upstream gene, nst-1. The analysis was done in three steps to examine the entire region between the genes. The first step gel and the RNA deep sequencing data show that K01C8.6 RNA is preferentially SL2 trans-spliced, as would be expected if this gene were downstream in an operon. Products extending from the 1485, 1200, and 932 primers are shorter than expected. This is presumably due to splicing of the transposon NPALTA1_CE from the RNA, as has been previously described with other transposons (Rushforth et al. 1993; Rushforth and Anderson 1996) or due to a reverse transcription or PCR artifact at the inverted repeats. Because all reverse transcription was performed with strand-specific primers and the reverse transcriptase heat inactivated prior to PCR, clec-142 mRNA cannot be detected in these assays. (B) The genomic arrangement of nduf-5 is depicted above. This gene is ∼2.6 kb downstream from mek-2. The gene Y54E10BL.3 lies on the opposite strand between these two genes. The transposon CELE1 is indicated as a double arrow upstream of nduf-5. Gels of overlapping RT-PCRs indicate that RNA is transcribed along the entire region between nduf-5 and the nearest upstream gene, mek-2. The analysis was done in three steps to examine the entire region between the genes. Arrows mark the site of faint products on the gels. The first step gel and the RNA deep sequencing data show that nduf-5 RNA is preferentially SL2 trans-spliced, as would be expected if this gene were downstream in an operon. Products extending from the 624 and 914 primers are shorter than expected, presumably due to splicing of the CELE1 transposon from the RNA or an artifact of reverse transcription or PCR at the inverted repeats. Because all reverse transcription was performed with strand-specific primers and reverse transcriptase heat-inactivated prior to PCR, Y54E10BL.3 mRNA cannot be detected in these assays.