Figure 4. FolQ, a missing folate synthesis enzyme in bacteria and plants.
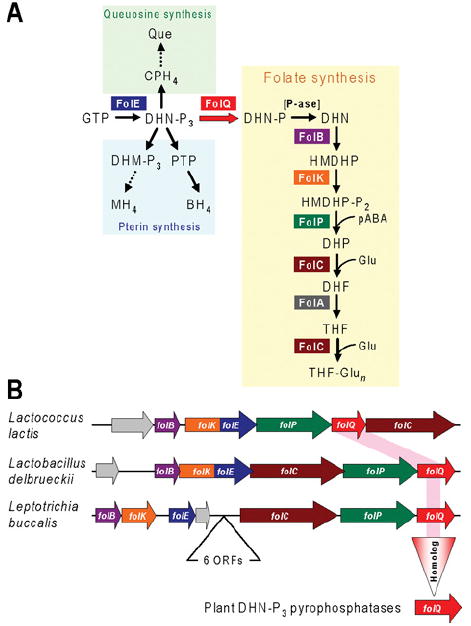
(A) The tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis pathway and its branches leading to queuosine and pterins. Note that the previously missing enzyme FolQ (YlgG in Lactococcus lactis) is the first step unique to the folate pathway. Abbreviations: BH4, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin; CPH4, 6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin; DHF, 7,8-dihydrofolate; DHM, 7,8-dihydromonapterin; DHN, 7,8-dihydroneopterin; DHP, 7,8-dihydropteroate; Glu, glutamate; HMDHP, 6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropterin; MH4, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydromonapterin; -P, phosphate; -P2, pyrophosphate; -P3, triphosphate; pABA, p-aminobenzoate; P-ase, non-specific phosphatase; PTP, 6-pyruvoyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin; Que, queuosine; THF, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate; THF-Glun, tetrahydrofolate polyglutamates. (B) Clustering in operonic arrangements of folQ with genes encoding other folate synthesis enzymes in two lactobacteria (phylum Firmicutes) and Leptotrichia buccalis (phylum Fusobacteria). Arrows indicate transcriptional direction; overlapping arrows indicate translational coupling. Genes are colour-coded in agreement with (A); non-conserved genes are coloured grey. A short intervening block of six genes separates the two clusters of folate synthesis genes in L. buccalis. The rose highlight linking the bacterial folQ genes and the vertical triangle represent the projection of the bacterial gene function to plants.
