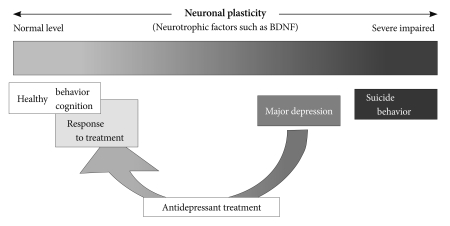
Figure 1.
The neuronal plasticity in major depression, antidepressant treatment, and suicide behavior. Major depression is associated with impaired neuronal plasticity in the brain. Suicide behavior can be a consequence of very severe impaired neuronal plasticity. Antidepressant treatments promote several forms of neuronal plasticity, including neurogenesis, synaptogenesis and neuronal maturation together with increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor activity, which can develop the antidepressant response. The neuronal plastic change can influence mood or recover depressed mood.