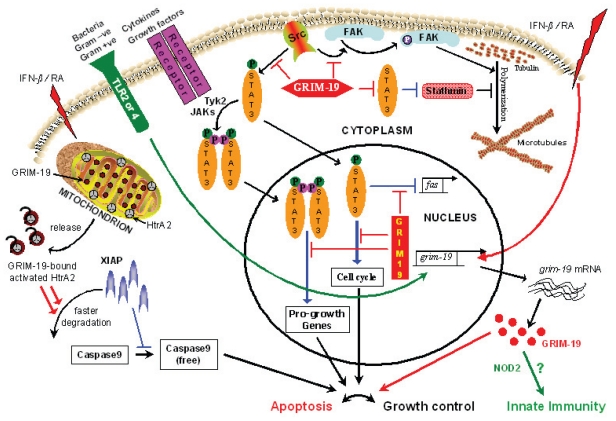
Figure 2.
Cellular roles of GRIM-19. GRIM-19 appears to have more functions than previously envisaged: 1) It targets growth-promoting proteins, STAT3 and Src, to achieve growth control; 2) It augments the activity of HtrA2 to cleave XIAP; 3) In conjunction with NOD2 it participates in innate immune responses. GRIM-19 can perform these functions only when it is present in more than one intra-cellular compartment. For example, nuclear and cytosolic GRIM-19 can effectively block STAT3 and Src, respectively. GRIM-19 overexpression effectively blocks cell motility by decreasing tubulin polymerization. Upon IFN/RA stimulation, the de-novo synthesized GRIM-19 participates in growth control in conjunction with other proteins. Requirement of GRIM-19 for complex-I assembly and stability vis-à-vis ATP generation, is one of its reported functions. Red colored-lines and arrows represent GRIM-19-dependent inhibitory and stimulatory pathways, respectively. Blue colored lines and arrows represent STAT3-dependent inhibitory and stimulatory pathways, respectively. Green arrows represent novel GRIM-19 inductive and functional pathways. P in green and pink colored circles indicate phosphorylations at Serine 727 and tyrosine 705 residues, respectively.