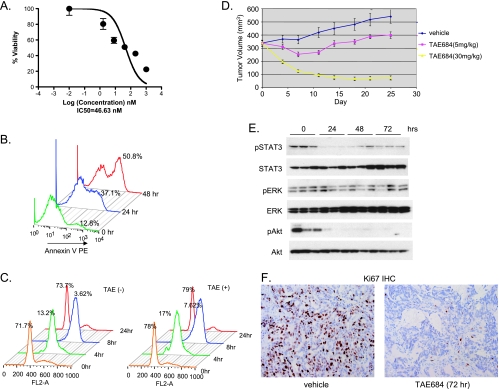
Figure 3.
Effect of TAE684 on H3122 NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo. (A) TAE684 reduces H3122 viability. Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of TAE684. Cell viability was measured by CellTiterGlo 72 hours after treatment. (B) TAE684 induces apoptosis. Cells were treated with 200 nM TAE684, and apoptosis was measured at the indicated time after dosing by annexin V stain. (C) TAE684 does not affect cell cycle progression. Cells were treated with 200 nM TAE684 for 24 hours, arrested at G1/S transition with HU, and released into the S phase. Cells were harvested at indicated time, stained with PI, and analyzed for cell cycle distribution. Percentage of cells in G1 at various time points is shown. (D) TAE684 inhibits established H3122 xenograft tumor growth. A total of 5 x 106 cells were implanted sc into nude mice. When the average tumor size reached 300 mm3, mice were randomized into different treatment groups. TAE684 was administered per os daily at the indicated doses or vehicle (10% 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone/90% PEG30). n = 10 for each treatment group. P = 10-7 (control vs TAE684 5 mg/kg), P= 5.6 x 10-30 (TAE684 5 vs 30 mg/kg). (E) TAE684 inhibits EML4-ALK signaling in H3122 xenograft tumors. Established H3122 xenogaft tumors were treated with 30 mg/kg TAE684, cell lysates were prepared at the indicated time, and Western blot analysis was performed to measure phosphorylated Akt, ERK, and STAT3. (F) TAE684 inhibits proliferation of H3122 tumor cells. Established H3122 xenogaft tumors were treated with 30 mg/kg TAE684, and Ki-67 and CC3 IHC was performed at the indicated time to measure cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively (n = 5 for each time point).