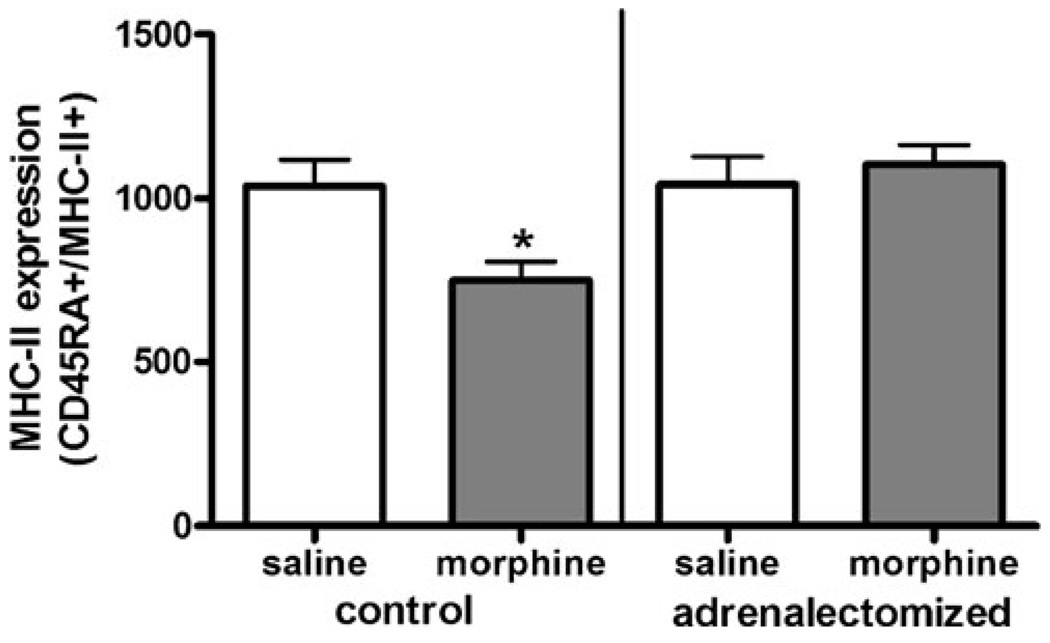
Fig. 3.
IL-4-induced MHC-II expression on B lymphocytes in morphine-treated adrenalectomized animals. Adrenalectomized Sprague–Dawley rats were purchased from Taconic Laboratories and given supplementary corticosterone for 1 week prior to experimentation. On the day of the experiment, animals were injected with either saline or morphine (10 mg/kg, s.c.) and euthanized after 2 h. Non-adrenalectomized intact animals were used as control groups. Two hours after injection, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated then cultured overnight with increasing concentrations of rrIL-4 (0.1– 1,000 ng/ml). Cultured cells were collected and washed prior to being incubated with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies as described in Fig. 1. Stained cells were fixed using 1% paraformaldehyde prior to analysis using a FACSort flow cytometer. Data are expressed as MFI ± SEM; (n=8). *p<0.05 (one-way ANOVA, Newman–Keuls)