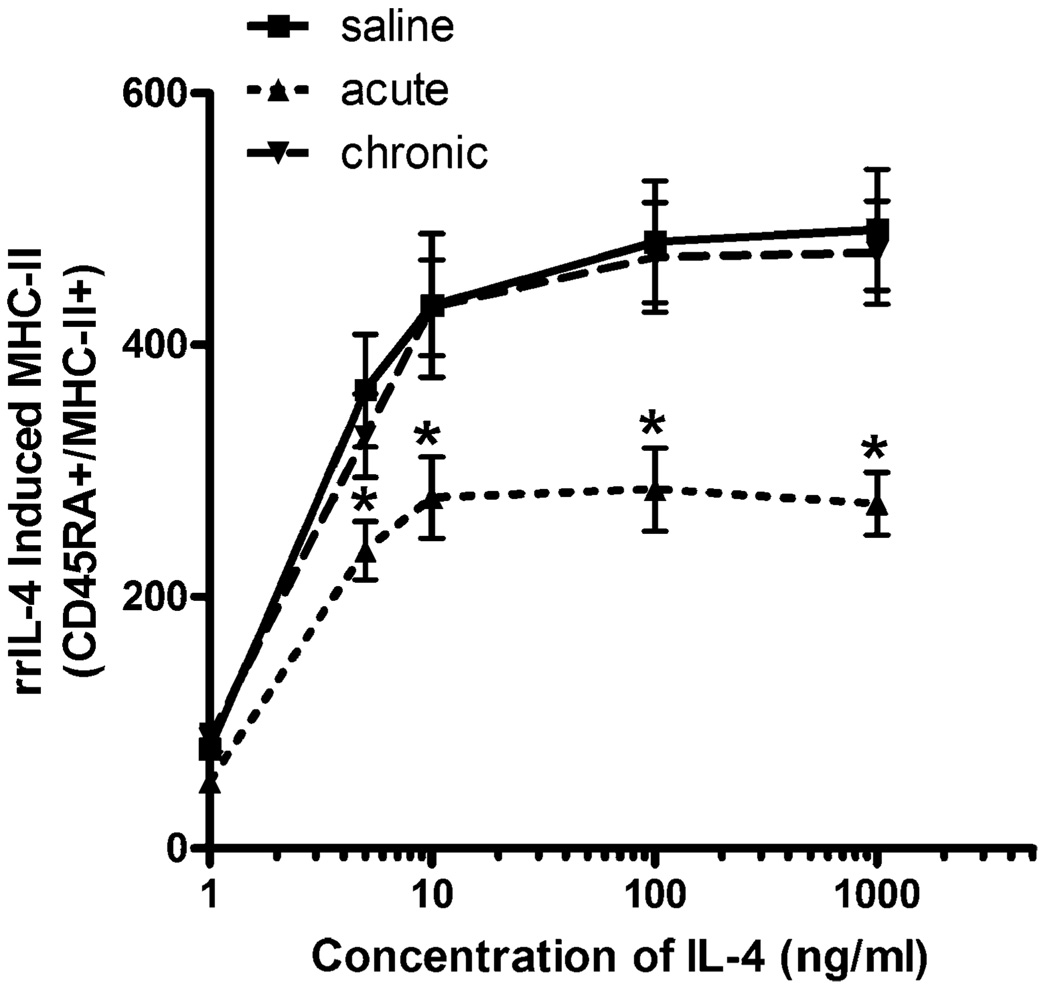
Fig. 4.
Effects of chronic morphine exposure on IL-4-induced MHC-II expression in B lymphocytes. Sprague-Dawley rats (n=8) were administered either saline or morphine twice daily using the dosing schedule as described in “Materials and methods”. Acutely treated animals received morphine (10 mg/kg, s.c.) on the day of the experiment. Two hours after the final injection, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated and cultured with rrIL-4 (0.1– 1,000 ng/ml). Stained cells were fixed using 1% paraformaldehyde prior to analysis using a FACSort flow cytometer. Data are expressed as MFI ± SEM. Data repeated in a subsequent experiment. *p<0.05 compared to all other treatment groups (ANOVA, Newman–Keuls)