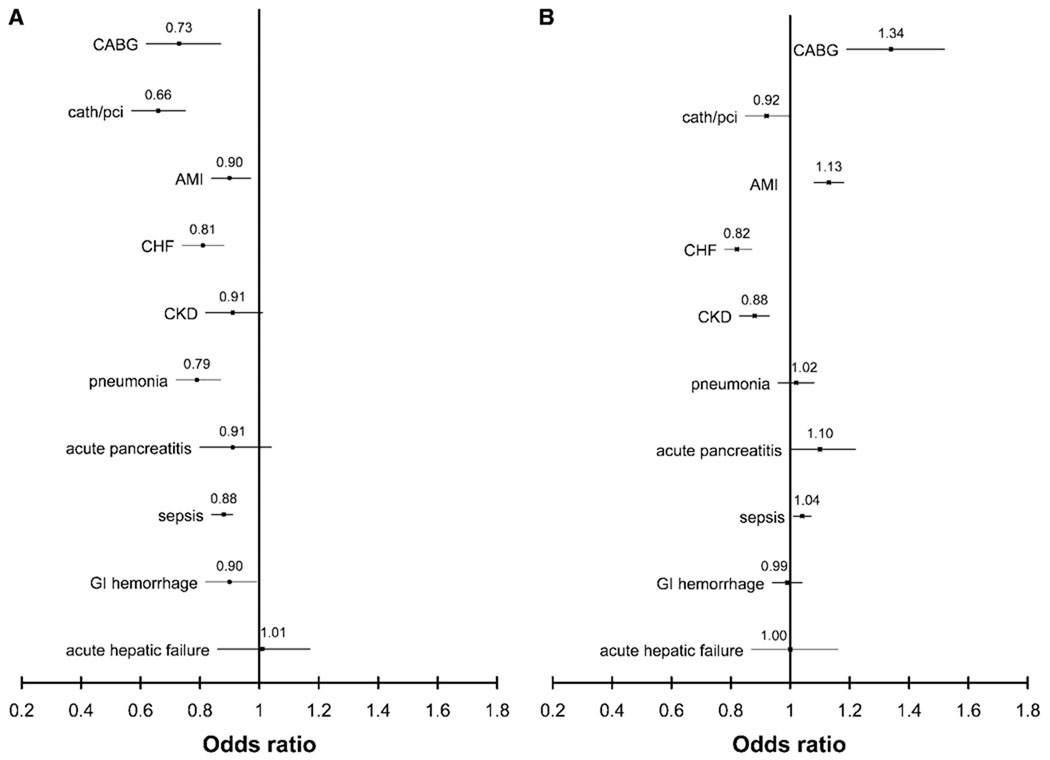
Figure 1.
Multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for death among black patients with ARF (A) and without ARF (B), stratified by selected concomitant procedures and diagnoses. Multivariable models adjusted for age, gender, need for mechanical ventilation, and D-CI. The reference group is white patients with the corresponding diagnoses and/or procedure. Point estimates are represented by the symbol and 95% confidence intervals by horizontal lines. Values <1 denote lower in-hospital mortality for black patients. Results are stratum specific (i.e., represent differences in odds for death for black versus white patients for a given procedure or diagnosis) and are not comparable across strata. P values for the interaction term (ARF * race) were as follows: CABG <0.001, catheter/PCI <0.001, AMI <0.001, CHF 0.72, CKD 0.31, pneumonia <0.001, acute pancreatitis 0.09, sepsis <0.001, gastrointestinal (GI) hemorrhage 0.25, and acute hepatic failure 0.86.