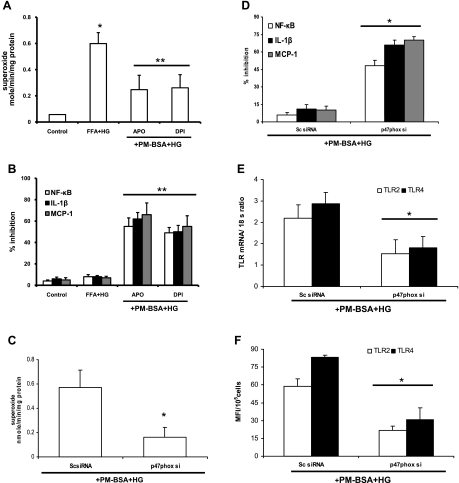
Fig. 5.
Role of NADPH oxidase. A: effect of NADPH oxidase inhibitors [apocynin (Apo) and diphenyleneiodonium (DPI)] on superoxide release by THP-1 cells. Cells pretreated with inhibitors were exposed to PM-BSA+HG, and superoxide release was measured as described in materials and methods. Values (in nmol·min−1·mg protein−1) are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. PM-BSA+HG. B: effect of NADPH oxidase inhibitors (apocynin and DPI) on NF-κB activity, IL-1β, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) release by THP-1 cells. Cells pretreated with inhibitors were exposed to PM-BSA+HG, and NF-κB activity, IL-1β, and MCP-1 release were measured as described in materials and methods. Values are expressed as mean ± SD % inhibition of control. **P < 0.01 vs. PM-BSA+HG. C: inhibition of NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox with small inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) affects PM-BSA+HG-induced superoxide release by THP-1 cells as described in materials and methods. Values (in nmol·min−1·mg protein−1) are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. scrambled control (Sc)-siRNA. D: inhibition of NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox with siRNAs affects PM-BSA+HG-induced NF-κB activity, IL-1β, and MCP-1 release by THP-1 cells as described in materials and methods. Values are expressed as mean ± SD % inhibition of control. *P < 0.05 vs. Sc-siRNA. E: inhibition of NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox with siRNAs affects PM-BSA+HG-induced TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA expression in THP-1 cells as described in materials and methods. Values are expressed as mean ± SD expressed mRNA/18S. *P < 0.005 vs. Sc-siRNA. F: inhibition of NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox with siRNAs affects PM-BSA+HG-induced TLR2 and TLR4 surface expression in THP-1 cells as described in materials and methods. Values are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. Sc-siRNA.